Among the various sprouted vegetables, sprouted potatoes are particularly toxic. Potato sprouts produce a toxin called solanine, which can corrode the stomach, cause hemolysis, and paralyze the nervous system. Regular cooking methods cannot eliminate this toxin. Some people opt to cut away the parts surrounding the sprouting area, but this may not effectively remove the toxin.
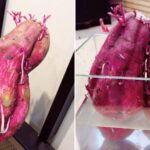
On the other hand, sweet potatoes that have sprouted are generally safe to consume, unless the tuber is moldy. Moldy sweet potatoes can produce the toxin ipomeamarone, which gives them a bitter taste.
Although it is safe to eat sprouted sweet potatoes, if you notice any signs of deterioration, it is best to discard them immediately.
Additionally, the nutritional value of sprouted sweet potatoes decreases as the vitamins and minerals are utilized to nourish the sprouts. The taste and flavor of the sweet potatoes also diminish with sprouting.

While edible, sprouted sweet potatoes will not taste as good as freshly harvested ones.
Sweet potatoes themselves are not poisonous, but when stored for extended periods, especially in humid environments, they become susceptible to mold. If you notice black or brown spots on the tuber, with or without sprouting, it indicates the presence of mold and the accumulation of the ipomeamarone toxin.
You can safely consume sweet potatoes that are just beginning to sprout and show no signs of black spots or mold. However, if the sprouts are more developed, it is advisable to discard them as their nutritional value has decreased, and their taste has altered significantly. On the other hand, sweet potatoes with signs of rot or black spots should be avoided altogether.
Research indicates that sweet potatoes stored at around 21°C for several weeks will start to sprout. Higher temperatures accelerate the sprouting process. This is a normal biological mechanism for sweet potatoes.
Conversely, sweet potatoes stored at temperatures between 12-14°C will not sprout.
It is recommended to avoid storing sweet potatoes in the refrigerator as the low temperatures can affect their texture and flavor, compromising their taste.
If you have sprouted sweet potatoes that you don’t intend to eat, you can use them as houseplants. Simply place a portion of the tuber in water, and the sprouts will gradually grow, forming an attractive pot plant. Alternatively, you can use the sprouted sweet potatoes as seeds and plant them in soil to grow a new crop.