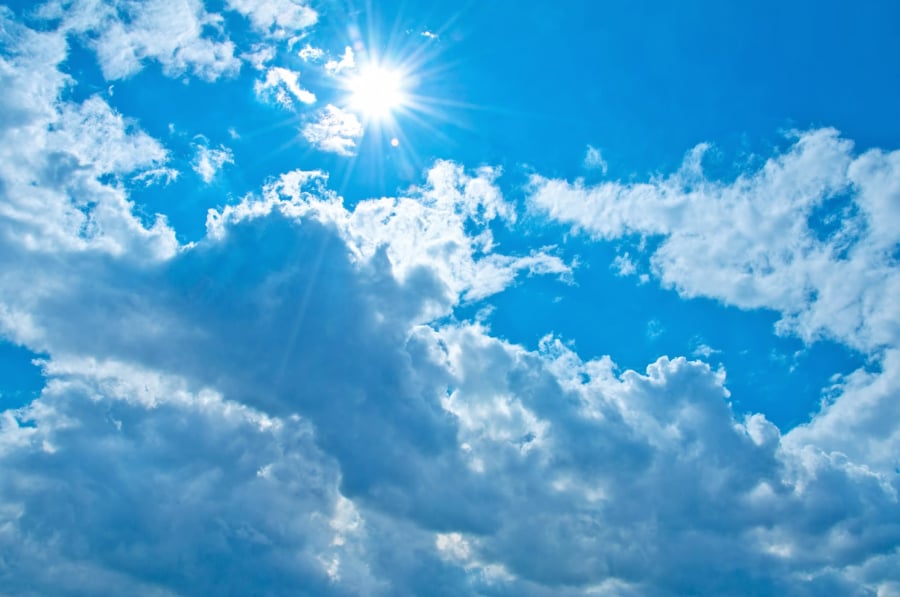
Why is the sky blue?
We see the sky as blue because of the way sunlight interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere. The electromagnetic spectrum, which we can see, includes different colors ranging from red light to violet light.

When all these colors mix together, the light turns into white light, shared Marc Chenard, a meteorologist at the US National Weather Service, with Live Science.
However, as white light travels from the Sun to Earth, some colors start interacting with the small molecules and atoms in the atmosphere.
Each color in the electromagnetic spectrum has a different wavelength. For example, red and orange have longer wavelengths while violet and sky-blue have much shorter ones.
Shorter wavelengths of light are more likely to be scattered or absorbed and dispersed in different directions by the air and gas molecules in the Earth’s atmosphere, explained expert Chenard.
Molecules in the atmosphere, primarily Nitrogen and Oxygen, scatter green and violet light in different directions through a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. That’s what makes the sky appear blue.
Although violet light is also scattered, there are a few reasons why we see the sky as blue more than violet, said astronomer Ed Bloomer from the Royal Observatory Greenwich in England.
According to him, first, the Sun doesn’t produce light with all colors being equal but contains more green light than violet light, so more green light gets scattered. Additionally, our eyes react differently to all colors, with less sensitivity to violet light, meaning we are able to see sky-blue more than violet.
The more common scattering of green light also affects the colors of sunrise and sunset. At sunset, when the Earth is at a further point from the Sun, the light has to travel a longer distance through the atmosphere to reach our eyes. By the time sunlight reaches us, all the blue light has been scattered away. The result is that orange, red, and yellow light remain to adorn the sunset.
Why is outer space black?
In space, there is no air, there’s nothing for light to bounce off, so it just travels in a straight line. No light gets scattered, and the “sky” appears dark and black.

Space always appears black due to the laws of light. Humans only see an object, in the case light from that object reaches our eyes and the image we see correlates to its size. Stars, no matter how numerous and bright, are just points of light in the vast universe, because they are too far away from us.
When light shines on and reflects off something, the atmosphere allows for “scattering” and the ability to see the colors in the spectrum that the eye sees. Space looks dark because there is no strong enough atmosphere to cause scattering.