There are several types of heaters available on the market, including ceramic heaters, oil-filled heaters, and infrared heaters, each with its own unique features, technical specifications, and advantages and disadvantages. However, their common function is to generate heat and warm up indoor spaces during cold weather.
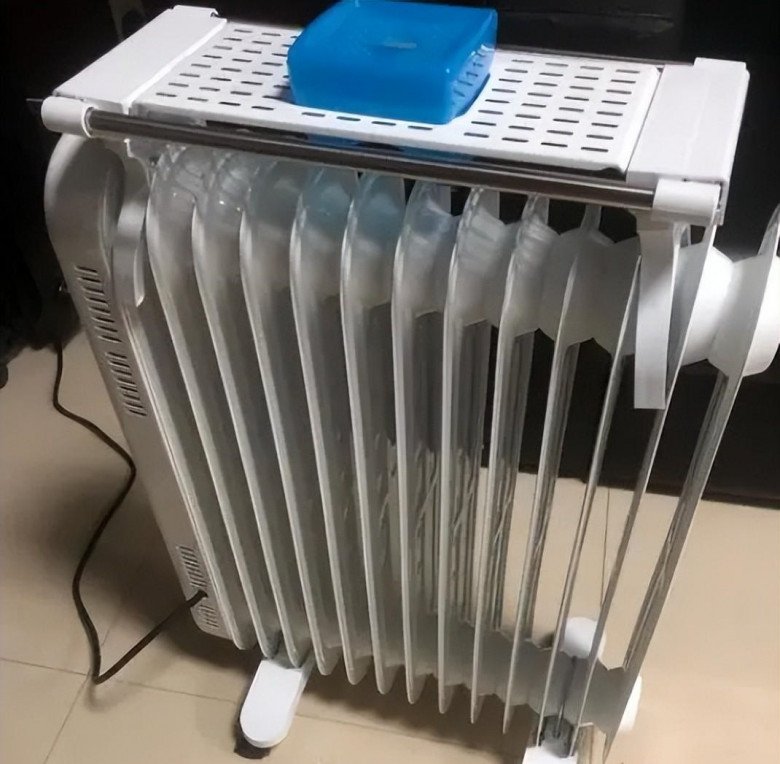

However, it is one of the most energy-consuming appliances during winter. Despite this, many people still use it due to its convenience and usefulness during the cold season.
When purchasing a heater, it is advisable to opt for those with an ECO energy-saving mode, ensuring that the technical specifications match the room size, and choosing a heater with a higher power consumption can lead to more efficient heating.
A standard heater power range for a comfortable room temperature is between 400 and 800 watts. To save energy and heat the room faster, you can choose a heater with a slightly higher power output, ranging from 800 to 1200 watts.
To optimize energy usage and prolong the life of the heater, avoid frequently turning it on and off, and refrain from setting the temperature to the maximum level.
2. Air Conditioner
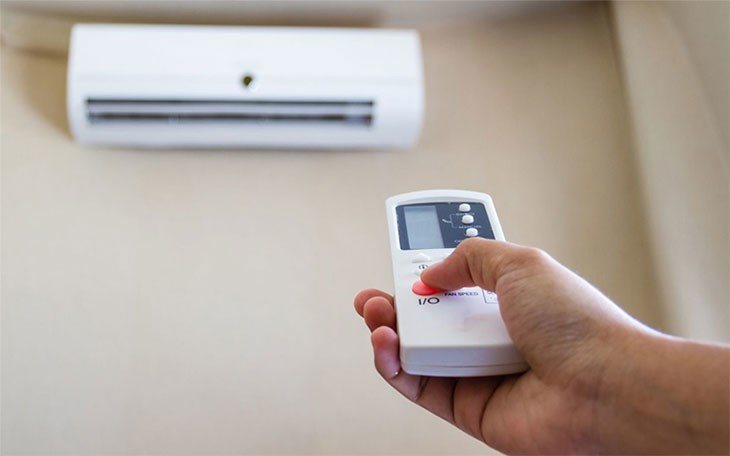

Two-way air conditioners are available in the market, offering both cooling and heating functions. While they are convenient, operating an air conditioner for heating during winter can result in significantly higher electricity consumption.
Typically, air conditioners are already considered power-intensive appliances. When used for heating, they consume two to three times more electricity compared to their cooling function.
Compared to other heating appliances, using an air conditioner in the winter can be much more expensive. Additionally, it’s worth noting that their heating performance may not be as effective when temperatures drop too low.
3. Water Heater
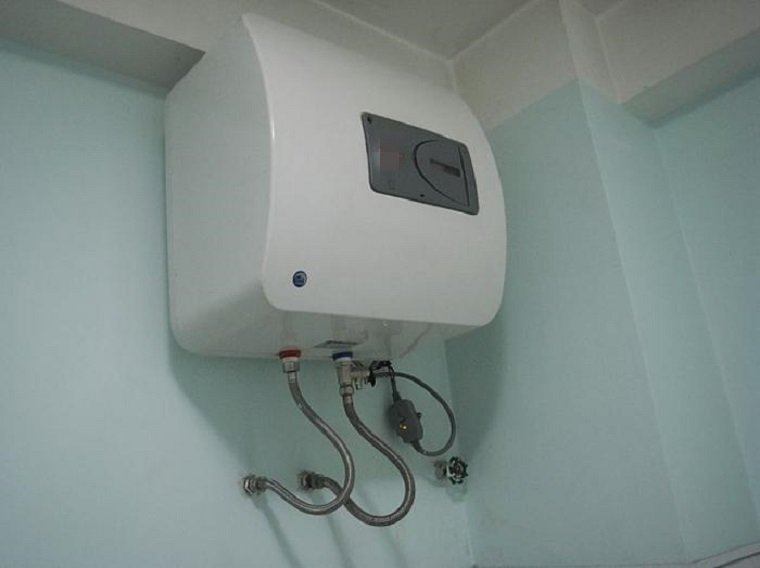

Water heaters are considered essential home appliances for many families. With just a flip of a switch, you can have hot water ready in a few minutes, which is especially convenient during winter.
However, water heaters are among the most power-consuming appliances in a household. According to EVN, most families use a 20-liter water heater, sufficient for 2 to 4 people’s daily needs.
For those who only turn on the heater before use, the average daily usage of one hour can result in a monthly consumption of 70 to 80 kWh. For families who keep the heater on continuously and use it more frequently, the consumption can reach up to 230 to 340 kWh per month.
4. Bathroom Heater

Many people install bathroom heaters to make bathing more comfortable during winter. As body temperature can drop suddenly during bathing, having a bathroom heater can help prevent cold-related illnesses and reduce the risk of hypothermia.
Bathroom heaters are typically designed as wall-mounted or ceiling-mounted fixtures, and their energy consumption can be comparable to that of water heaters.
5. Electric Thermopot
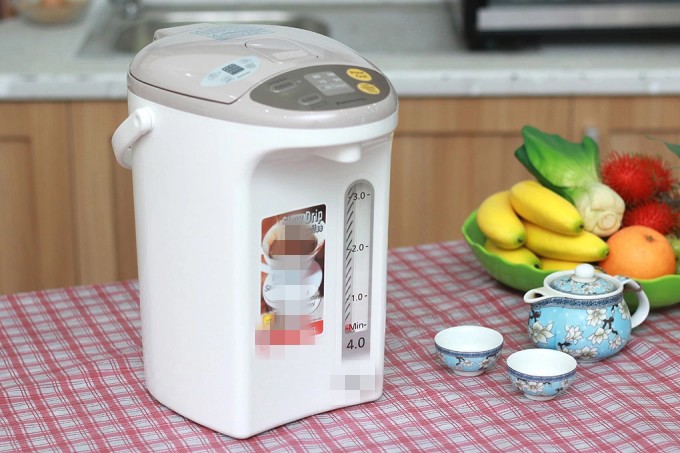

Electric thermopots are commonly used in Vietnamese households to obtain hot water daily, especially during winter. With a capacity ranging from 4 to 6 liters, these pots continuously boil water and maintain its temperature for up to 6 hours or the minimum temperature set by the manufacturer.
The power consumption of an electric thermopot can vary from 700 to 1,200 watts, depending on the manufacturer and capacity. If used continuously and with an average daily hot water consumption of 6 to 8 liters, the monthly electricity consumption can reach 40 to 100 kWh.
The Power Drainers: Unplug These Devices After Use or Risk a Shocking Electricity Bill
“It was an eye-opener when an electrician friend of mine pointed out how certain electrical appliances, if left on standby mode for extended periods, can rack up substantial electricity costs. This got me thinking about how many of us are unaware of these hidden energy drains and the subsequent impact on our wallets and the environment.”