Microplastics, with sizes ranging from 1 nanometer to 5 millimeters, are the decomposed components of plastic products such as bottles, bags, and various other discarded plastic items. They are present in a variety of foods and beverages, with a recent focus on their presence in tea, one of the most globally consumed beverages.
A 2019 study by McGill University in Canada found that when tea bags are steeped in hot water at 95°C, up to 11.6 billion microplastic particles and 3.1 billion nanoplastic particles can be released. This is due to the fact that most tea bags today are made from plastic materials such as nylon or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Furthermore, adding sugar to tea can exacerbate the problem, as a 2022 study revealed that many types of sugar in the US are contaminated with microplastics.
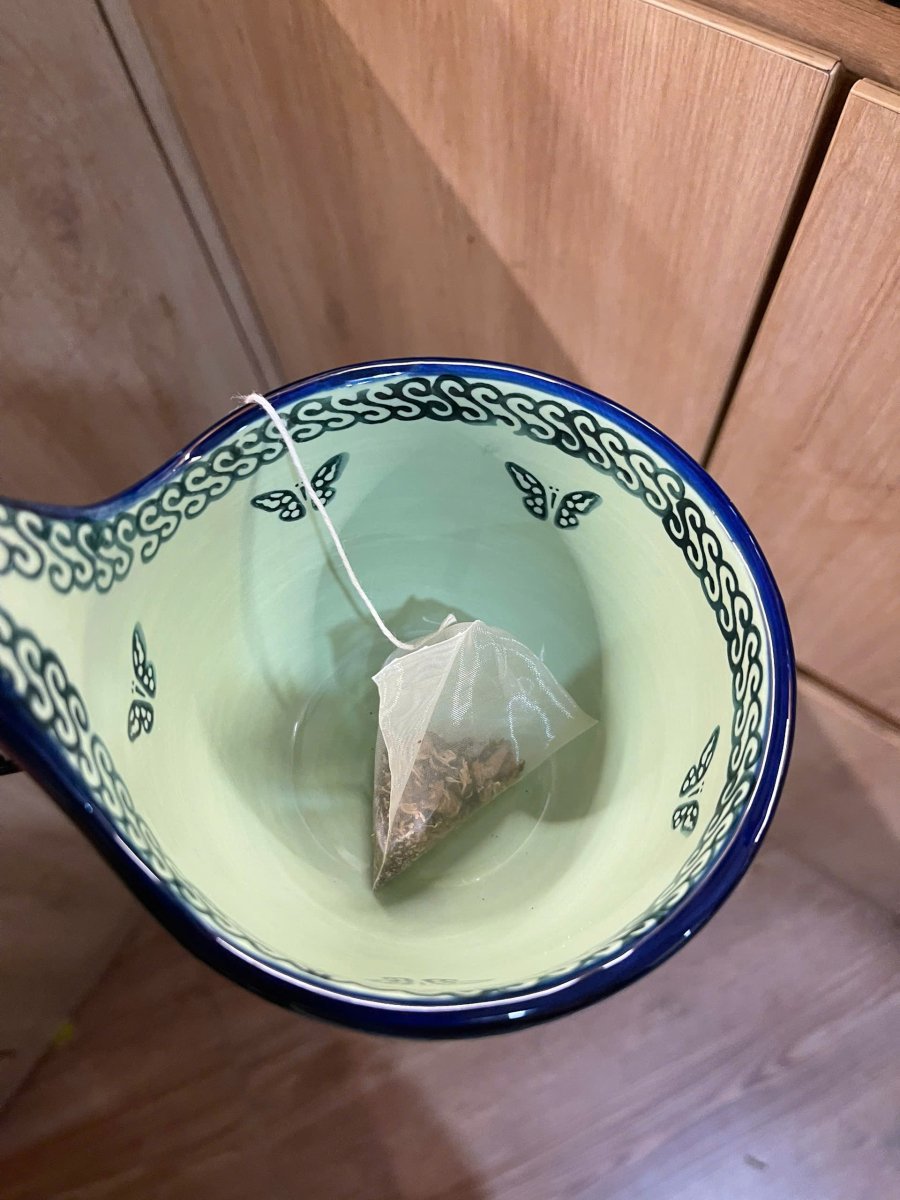

Microplastics, with sizes ranging from 1 nanometer to 5 millimeters, are the decomposed components of plastic products such as bottles, bags, and other discarded plastic items.
Researchers from the University of Nevada, USA, tested tea bags made from polypropylene, nylon, and cellulose. Their findings showed that all three types of tea bags released microplastics, with the polypropylene bag releasing the highest amount.
A separate study from the University of Barcelona, Spain, published in the journal Chemosphere in December 2024, attracted significant attention. It found that just 1 milliliter of hot water could contain up to 1.2 billion nanoplastic particles after soaking 300 tea bags at 95°C. Worryingly, these particles can be easily absorbed by human intestinal cells.
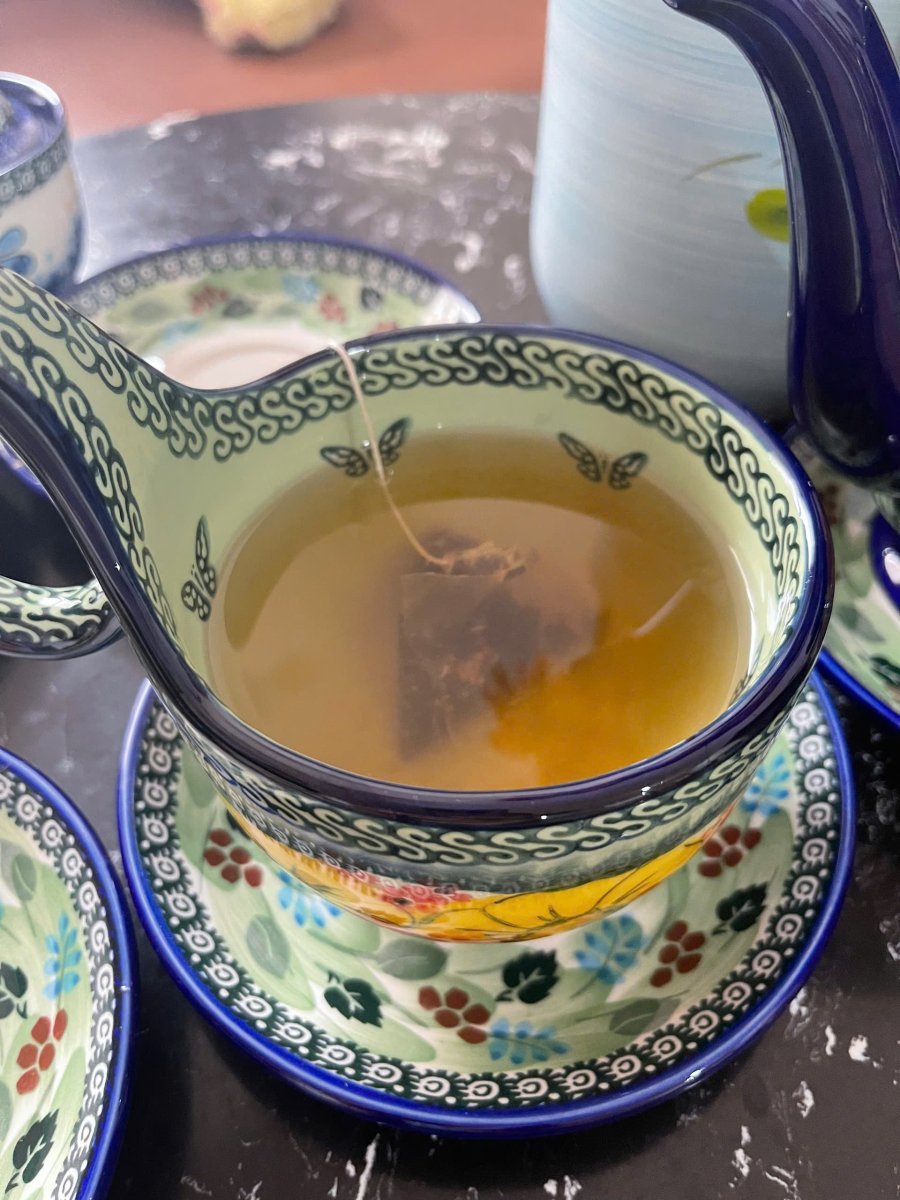

These particles can easily be absorbed by human intestinal cells, causing potential health risks.
A study conducted in March 2024 revealed that individuals with the presence of microplastics in their carotid arteries had twice the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, or even death compared to those without. Once microplastics enter the body, they can disrupt natural biological processes and carry harmful substances such as bisphenol, phthalates, flame retardants, PFAS, and heavy metals, distributing them into the blood and organs like the liver, kidneys, and brain. This can negatively impact respiratory health, cause allergies, nerve damage, and increase the risk of cancer.
To minimize microplastic intake while still enjoying tea, Dr. Alba García-Rodríguez, a researcher at the University of Barcelona’s Department of Genetics and Microbiology, recommends using loose tea leaves with a stainless steel infuser or a reusable stainless steel tea filter.
The Hidden Dangers of Four Seemingly Safe Foods: Low in Chemicals, but Prone to Parasitic Infection
Prioritizing fresh and chemical-free food for your family’s meals is commendable, but it’s important to be aware of the hidden dangers lurking in seemingly harmless foods. Unbeknownst to many, certain foods, if not prepared properly, can pose a serious risk of parasitic infections, particularly from worms. It is crucial to be vigilant and informed to safeguard your family’s health.