A study conducted by the Harvard Medical School revealed that substituting butter with olive oil when eating bread could contribute to increased longevity. This research focused on analyzing the impact of different food choices on the lifespan of US adults.
The study, published in the JAMA medical journal, found that individuals who consumed more butter had a higher risk of premature death compared to those who used olive oil. Specifically, increasing olive oil intake by 10g per day reduced the risk of cancer by 11%, while increasing butter consumption raised this risk by 12%.
While further in-depth research is needed to confirm the link between olive oil, butter, and cancer risk, this study underscores the importance of diet in long-term health. Professor Tom Sanders from King’s College London commented, “The study provides clear evidence that those who use vegetable oils in their meals tend to live longer than those consuming large amounts of butter.”
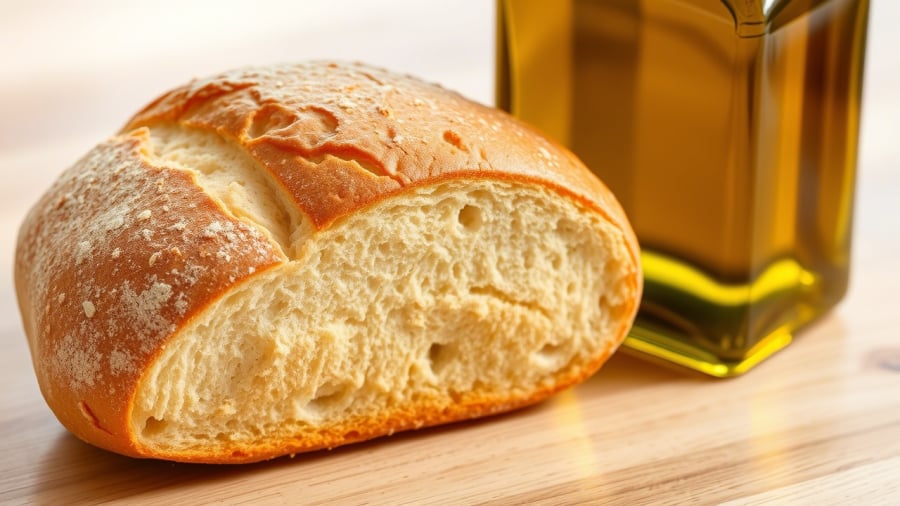

Further research is needed to establish a direct connection between olive oil, butter, and cancer risk, but the study emphasizes the significance of dietary choices for long-term wellness.
Olive oil, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, has long been lauded by Harvard Health experts for its exceptional health benefits. Numerous previous studies have also confirmed that the Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. While the nutritional benefits of this diet come from various sources, olive oil appears to play a pivotal role.
Professor Tom Sanders further explained, “The health benefits of olive oil are attributed to its strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Observational studies have shown that individuals who consume more olive oil have a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, certain cancers, and even dementia compared to those who use little or no olive oil.”
The British Heart Foundation also recommends olive oil for its significant cardiovascular advantages. As an integral part of the Mediterranean diet, they suggest incorporating olive oil into daily meals, such as using it in salad dressings, rather than merely taking it as a supplement. However, it’s important to note that the recommended maximum fat intake for adults is around 70g per day.
This study not only offers insights into the role of olive oil in a healthy diet but also encourages individuals to make smarter food choices to safeguard their long-term health.