Inadequate zinc intake can impact the activation and function of neurons in these areas. Zinc contributes to maintaining the structure and integrity of synapses, where information is transmitted between neurons.
Low zinc levels can impair the formation of new neural connections, leading to decreased memory efficiency. Children and adolescents, who are in a critical phase of development and learning, particularly need sufficient zinc to support memory formation and cognitive abilities. Zinc deficiency can result in cognitive delays, affecting their focus, learning capacity, and problem-solving skills.
Additionally, zinc plays a significant role in regulating hormones and neurotransmitters, which influence mood and emotions. A zinc-deficient diet may lead to anxiety and other psychological issues. Therefore, ensuring adequate zinc intake helps children improve their memory and maintain their psychological well-being.
To boost zinc intake, parents should encourage their children to consume zinc-rich foods. Establishing healthy eating habits early on will optimize children’s physical and intellectual development. A balanced and nutritious diet will also enhance brain function, thereby improving their learning abilities and memory retention.
Experts suggest incorporating the following seven zinc-rich foods, packed with brain-boosting nutrients, into your child’s diet:
Oysters
Beef

Chicken

Sunflower Seeds

Lentils

Dairy Products

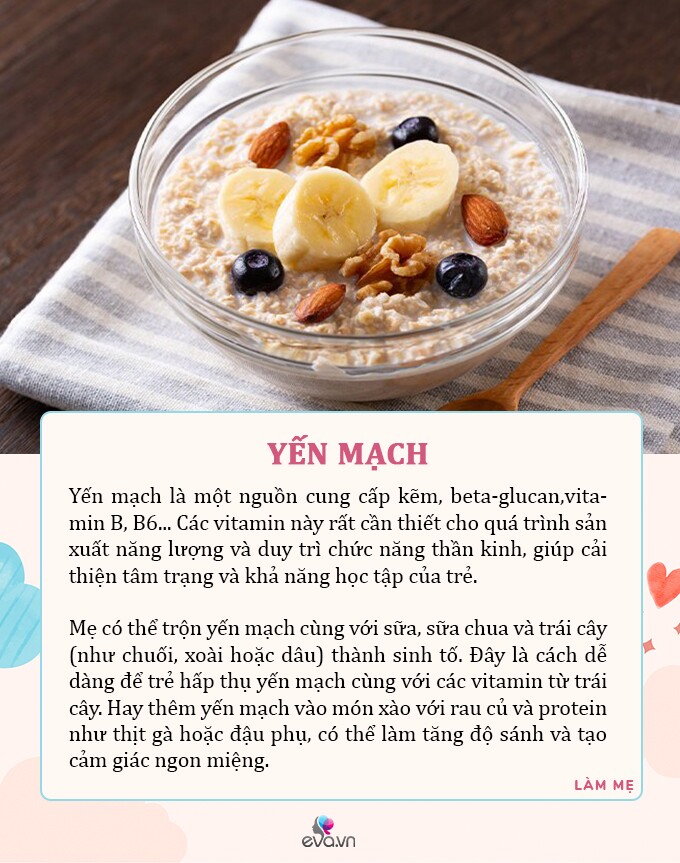
Oats
Unveiling the Four Drastic Differences Between Late and Early Sleepers
The age-old debate on early vs. late bedtimes for children has sparked much discussion among experts. Four key differences have been highlighted, which all parents should be aware of, to ensure their children’s sleep patterns are healthy and beneficial. These insights will help parents make informed decisions about their children’s sleep routines and encourage positive adjustments for their well-being.





































