Multiple Bank Accounts Compromised by Malware on Smartphones
In recent times, numerous cases of individuals losing money from their bank accounts have been reported, stemming from victims’ smartphones contracting malware or spyware applications.
Malware and spyware
These malicious software and applications enable hackers to infiltrate banking apps installed on users’ smartphones or intercept text messages containing verification codes, allowing them to log in to bank accounts and drain the funds they contain.

Smartphone users are increasingly becoming the targets of hackers and fraudsters (Photo: Getty).
A recent example is the case of Nguyen Thi Giang Huong, Chairperson of Nhon Trach District People’s Committee, Dong Nai Province, who fell victim to a sophisticated cyber fraud group. The attackers gained access to her smartphone, allowing them to illegally access her bank account and steal an amount totaling 170 billion VND.
In February of this year, a man residing in Hanoi’s Hoan Kiem District lost 3 billion VND from his bank account after mistakenly installing malware on his smartphone. The fraudsters disguised the malware as an app that provides public services, tricking the victim into installing it on his smartphone. The attackers then hacked into the victim’s stock trading app and illegally seized the 3 billion VND.
Earlier in January, the Hanoi City Police Department reported that six victims had also fallen prey to cybercriminals using malicious apps that masquerading as public service applications. The criminals stole a total of nearly 20.6 billion VND, with the highest individual victim losing 15 billion VND.
Deceptive Tactics to Trick Victims into Installing Malware and Spyware
To obtain victims’ personal information and gain unauthorized access to their smartphone bank accounts, the primary strategy employed by cybercriminals is to deceive victims into installing apps that contain malware and spyware.
The most prevalent tactic is for the criminals to pass off malicious apps as public service applications.

Malicious apps disguised as public service apps to steal victims’ assets (Photo: VCS).
The perpetrators may contact their intended victims via phone call or directly through Zalo, posing as representatives of government agencies. They then instruct users to install specific apps provided by them, claiming they are necessary for accessing public services or for reporting demographics or other personal data.
Since these apps contain malware and are not officially distributed through legitimate app stores like Android and iOS, the fraudsters provide detailed instructions on how to install them, including granting permissions that allow these apps to access deep within the smartphone to access sensitive information, such as intercepting text messages, stealing login credentials, or remotely taking control of the device.
Some sophisticated malicious and spyware apps even request that users provide facial or fingerprint data, which the attackers can use to steal the victim’s biometric information to facilitate their theft.
Another common method used by the criminals is to spread provocative and curiosity-inducing content on social media, such as images or videos of accidents, terrorism, or explicit clips, accompanied by a QR code and a message encouraging the user to “scan to view the full content.”
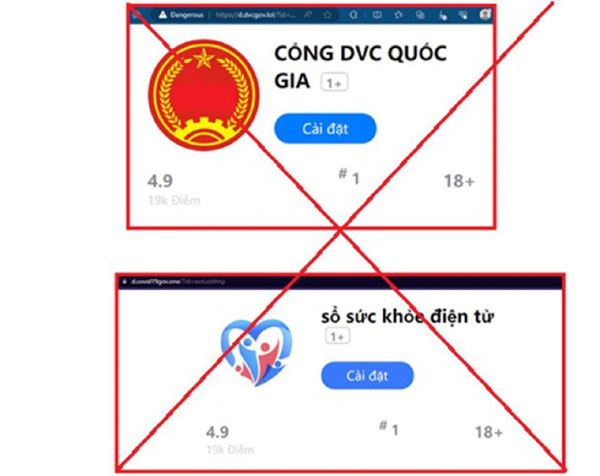
Many fraudsters exploit victims’ curiosity and trick them into installing malware through QR codes (Screenshot).
Unable to resist their curiosity, many individuals have recklessly scanned these QR codes, which lead to spoofed websites created by hackers or automatically download apps containing malware or spyware. The fraudsters subsequently guide users in installing these apps to access the full extent of the captivating content.
However, after installing these apps, the victim’s smartphone becomes compromised, allowing the attacker to steal personal information or drain their bank accounts or investment portfolios.
Signs of Smartphone Malware Infection
Compared to Apple’s iOS platform, Google’s Android platform is considered less secure due to numerous security vulnerabilities and is frequently targeted by hackers, malware, and spyware.
One reason why hackers are more interested in Android is due to its popularity since it remains the most widely used mobile operating system globally.
However, recently, there has also been an increase in malware targeting iOS devices, and unsuspecting users may also become victims of cybercriminals if they are not sufficiently cautious.
So how can you determine if your device has been infected with malware?
The following indicators can assist you in identifying whether your smartphone is infected with malware or spyware, enabling you to take appropriate actions to protect your privacy and personal data.
Progressive slowdown and sluggishness of the device, even without a recent operating system update
Malware and spyware typically run in the background of a device. Thus, if spyware has infiltrated the system, it will consume a considerable amount of system resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) to continuously run in the background and monitor the user’s activity.
If you notice that your smartphone is becoming increasingly slow and sluggish, even though you have not recently upgraded your operating system, or even after uninstalling some apps and observing no improvement, consider the possibility that your device may have been infected with spyware.
Battery drains rapidly despite minimal usage
In addition to causing a smartphone to run sluggishly by consuming CPU and RAM, the background processes of malware can also lead to a faster battery drain.
Users should access the “Battery Management” section on their Android or iPhone devices to determine which apps are consuming the most battery. If a suspicious app appears, it is advisable to remove it from the device promptly.
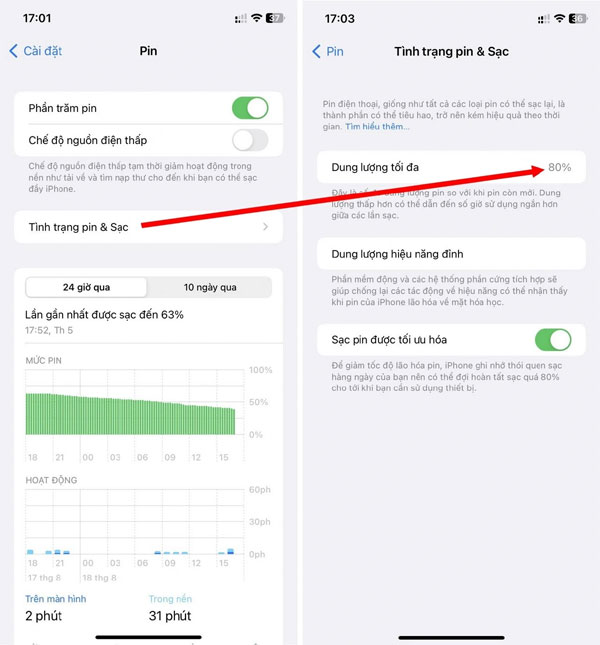
Checking the battery status of the device will help you determine if the rapid battery drain is due to a worn-out battery or malware (Screenshot).
In many cases, a rapidly draining battery may be due to a worn-out battery after prolonged use. You may refer to the guidelines provided by the website here to assess your smartphone’s battery degradation and determine whether the rapid battery drain is caused by a worn-out battery or malware, enabling you to take appropriate remedial measures.
If the smartphone’s battery is severely degraded, it is recommended to replace it to avoid potential risks of fire or explosion during use.
Smartphone frequently overheats despite minimal usage
As mentioned earlier, the operation of malicious apps in the background can not only cause a smartphone to run sluggishly and drain the battery but also lead to overheating even with minimal activity.
Therefore, if you notice that your smartphone is frequently overheating despite minimal usage, this may be an indication that the device has been infected with malware.
Strange icons appear in the system tray
Occasionally, you may notice strange icons appearing in the system tray, but if you are unsure which app they belong to, consider the possibility that your smartphone may have been infected with malware.
The appearance of strange icons can also indicate a possible malware infection (Screenshot).
However, dangerous malicious apps often conceal themselves meticulously and rarely leave visible traces. Consequently, if you notice strange icons in the system tray, it is more likely that they belong to malware with simple functionalities, such as adware that displays intrusive advertisements. Nevertheless, users should remain vigilant against these types of malware as well.
Automatic sending/receiving of data while connected to the internet
If your smartphone is connected to the internet but you are not actively using any internet applications (browsing the web, watching videos on YouTube, or using social media), and there are no ongoing updates on your device, yet data is still being sent or received, it is highly likely that your device has been compromised by spyware. This spyware may be sending or receiving data from your smartphone without your knowledge.
To determine whether your device is sending or receiving data over the internet, Android users can utilize the Internet Speed Meter app (available for free download here). iPhone users, on the other hand, can use the Traffic Monitor app (available for free download here).
These apps not only allow you to monitor your overall internet usage (via Wi-Fi or 4G) but also display the current network connection speed (download and upload rates). This will help you determine whether your smartphone is automatically sending or receiving data over the internet.
Full-screen advertisements appear unexpectedly
If your smartphone occasionally displays full-screen advertisements that cover the entire home screen, even when no apps are running, it is highly probable that your device has been infected by adware.
Some malware displays full-screen advertisements on a smartphone (Screenshot).
This type of malware may not be as dangerous as spyware, but it can be very disruptive and is commonly used by hackers to exploit users and generate illicit revenue through advertising content.
Web pages redirect automatically
This is not a frequent occurrence, but if you notice that your web browser is automatically opening or redirecting to unfamiliar websites, your smartphone may have been infected by malware.
In some
The primary strategy is deception, often posing as representatives of government agencies and instructing users to install specific apps for accessing public services or reporting personal data. These apps, distributed outside legitimate app stores, contain malware that grants access to sensitive information. Some sophisticated malicious apps even request facial or fingerprint data, enabling the theft of biometric information.
Another common method is spreading provocative content on social media with QR codes that, when scanned, lead to spoofed websites or automatically download malicious apps. Fraudsters then guide users to install these apps, compromising their smartphones and enabling personal information theft or financial loss.
Indicators of a potential malware infection include a progressive slowdown and sluggishness of your device, rapid battery drain despite minimal usage, frequent overheating, strange icons appearing in the system tray, automatic sending/receiving of data while connected to the internet, unexpected full-screen advertisements, and web pages redirecting automatically.
Google’s Android platform is considered less secure than Apple’s iOS due to numerous security vulnerabilities. One reason for hackers’ preference for Android is its popularity as the most widely used mobile operating system globally. However, iOS devices have also increasingly become targets, and users of both platforms must remain cautious to avoid falling victim to cybercriminals.




































