Hepatitis B is a highly infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), according to medical professionals. The disease can damage the liver and destroy liver cells, and it is a leading cause of liver cancer in Vietnam.
In addition to medical treatment, patients with hepatitis B also depend on their diet. Drinking an herbal tea made from the Phyllanthus niruri plant, also known as stone breaker or chanca piedra, is a traditional remedy recommended by Eastern medicine practitioners to help cool the liver and promote diuresis.
According to Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital, Phyllanthus niruri is a wild plant that grows everywhere without needing any care. In the past, people used to think of it as a weed and pull it out when they saw it growing in their gardens. Nowadays, it is cultivated on fields and farms to be used as a medicinal herb. Some people also plant it in their gardens, and when the plant grows, they dry it in the sun, clean it, and then boil it to make a tea to help cool their livers.
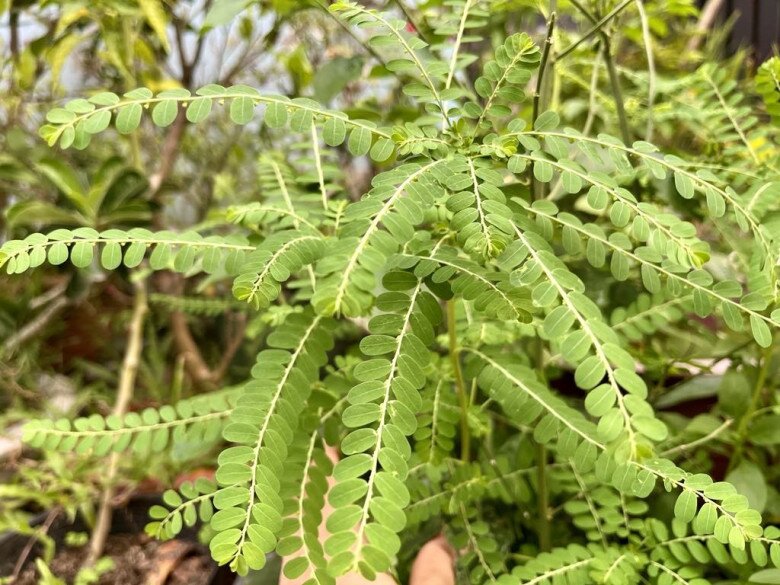

Phyllanthus niruri plant grown by a resident in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Photo by Dieu Thuan.
Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital explains that the plant is called “cho de rang chua” (“dog gives birth to teeth”) because locals observed that mother dogs would look for this plant to eat after giving birth. This behavior helps the mother dogs heal their wounds post-delivery.
In Eastern medicine, Phyllanthus niruri has a bitter and slightly sweet taste with a cooling property. It is believed to have the ability to clear liver heat, promote diuresis, cool the blood, detoxify, and sterilize.
Research conducted in Japan and India has identified active compounds in Phyllanthus niruri, including phyllantin, triacontanal, and hypophyllantin, which have therapeutic effects on hepatitis and fatty liver.
Additionally, the plant contains an important substance called phyllanthus, which strongly inhibits the HBV virus by suppressing its DNA polymerase enzyme, thereby reducing HbsAg and Anti-HBs.
For many years, extensive research has been conducted worldwide and in Vietnam on the medicinal properties of Phyllanthus niruri, especially its effects on liver and gallbladder disorders. With a daily dose of 900mg, up to 50% of the hepatitis B virus in the blood was reduced after one month of treatment.
In addition to the above-mentioned compounds, Phyllanthus niruri also contains high levels of antioxidants, which can help lower liver enzymes, protect the liver, and inhibit the activity and replication of the hepatitis virus. It also increases glutathione levels in the liver, thereby reducing the activity of SGOT and SGPT enzymes, which are indicators of liver damage during acute hepatitis episodes.
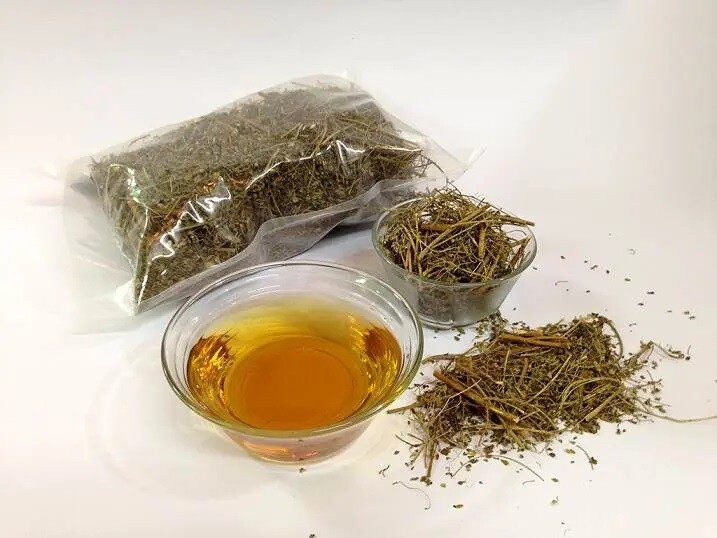

Dried Phyllanthus niruri plant prepared for herbal tea. Illustrative image.
Medicinal Uses of Phyllanthus niruri
In addition to treating hepatitis B caused by HBV, Phyllanthus niruri is also used to treat various other ailments. To enhance its therapeutic effects, it is often combined with other medicinal herbs. Here are some specific prescriptions:
For hepatitis with jaundice: 40g of Phyllanthus niruri, 12g of plantago major, 12g of gardenia jasminoides, and 16g of artemisia capillaris. Decoct all the ingredients together. Drink one decoction per day for 30 consecutive days.
For painful boils: Take a handful of Phyllanthus niruri, crush it with a little salt, add some boiling water, mix well, and squeeze out the juice. Drink the juice, and apply the pulp to the affected area.
For kidney stones: Use 24g of Phyllanthus niruri and decoct the water to drink. If you experience bloating, you can add fresh ginger or Job’s tears during the boiling process. When the condition stabilizes, occasionally use Phyllanthus niruri to make tea instead of drinking plain water. Consume 8-10g per day, not exceeding 30 consecutive days.

Phyllanthus niruri plants are now cultivated for medicinal purposes. Illustrative image.
Precautions When Using Phyllanthus niruri
According to medical professionals, Phyllanthus niruri is a safe, accessible, and effective medicinal herb. However, when using this herb, it is essential to keep the following in mind:
– Do not use large doses without consulting a doctor.
– Pregnant women should not use any medication containing Phyllanthus niruri.
– It is not recommended to use Phyllanthus niruri in large quantities or for extended periods for patients with a cold body constitution. When ingested, the substances in the plant may worsen the condition, inhibit the body’s heat production, and lead to other health issues.