What’s the difference between brown eggs and white eggs?
Nutrition expert Crystal Scott told Eat this not that: “The difference between brown eggs and white eggs is simply the color of the eggshell. Typically, with industrially-raised chickens, chickens with red or brown feathers and dark earlobes will lay brown eggs. On the other hand, chickens with white feathers and light earlobes will lay white eggs. Each different breed of chicken will lay eggs with different colors. Therefore, the color of the eggshell depends entirely on the type of chicken and the genetic inheritance of that chicken breed.”
Nutrition expert Megan Hilbert added that besides white and brown eggs, some types of chickens even lay eggs with speckles on the shell or light blue or light green eggs.
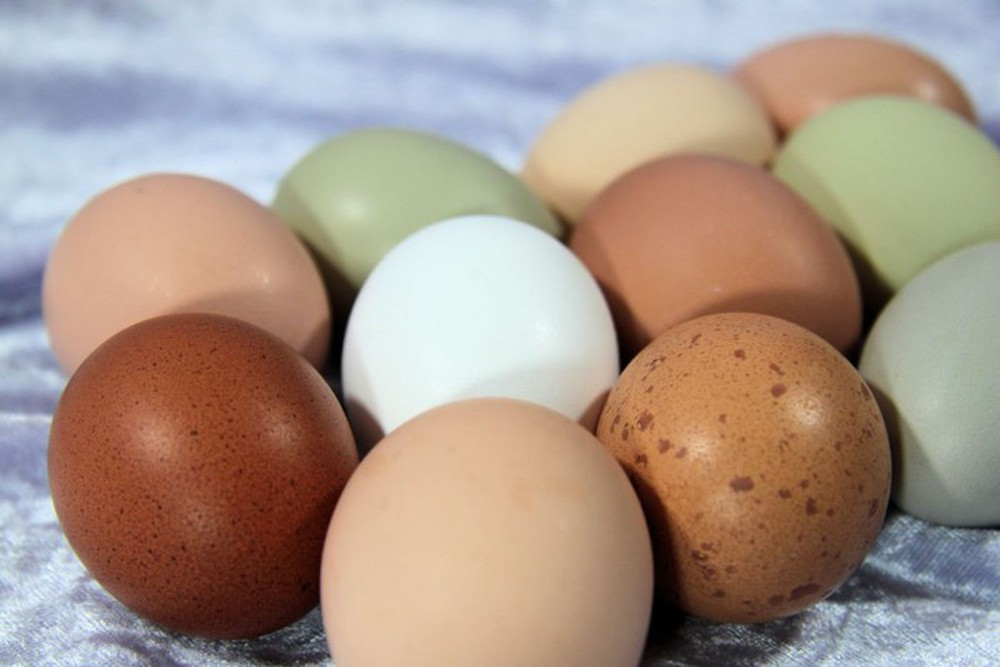

In addition to eggs with white or brown shells, there are also eggs with speckles on the shell, light blue eggs, or light green eggs.
Are brown eggs or white eggs more nutritious and better for health?
Hilbert said that some people believe that brown eggs are fresher or more “natural” than white eggs, and some even believe that white eggs are bleached and the nutrients inside have been altered.
However, Scott pointed out that this is completely untrue because the color of the eggshell does not determine the nutritional value of the egg. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), both brown and white eggs are still a source of protein, selenium, vitamin A, and vitamin B, as well as choline, which is good for the brain.
Therefore, all types of eggs are good for health. Scott said, “The nutritional content of eggs mainly depends on the diet and living conditions of the mother hen.”
But in general, eggs are one of the main foods in a diet because they are a great source of vitamin A, B, D, E, K, omega-3, zinc, and excellent choline, which are good for health.
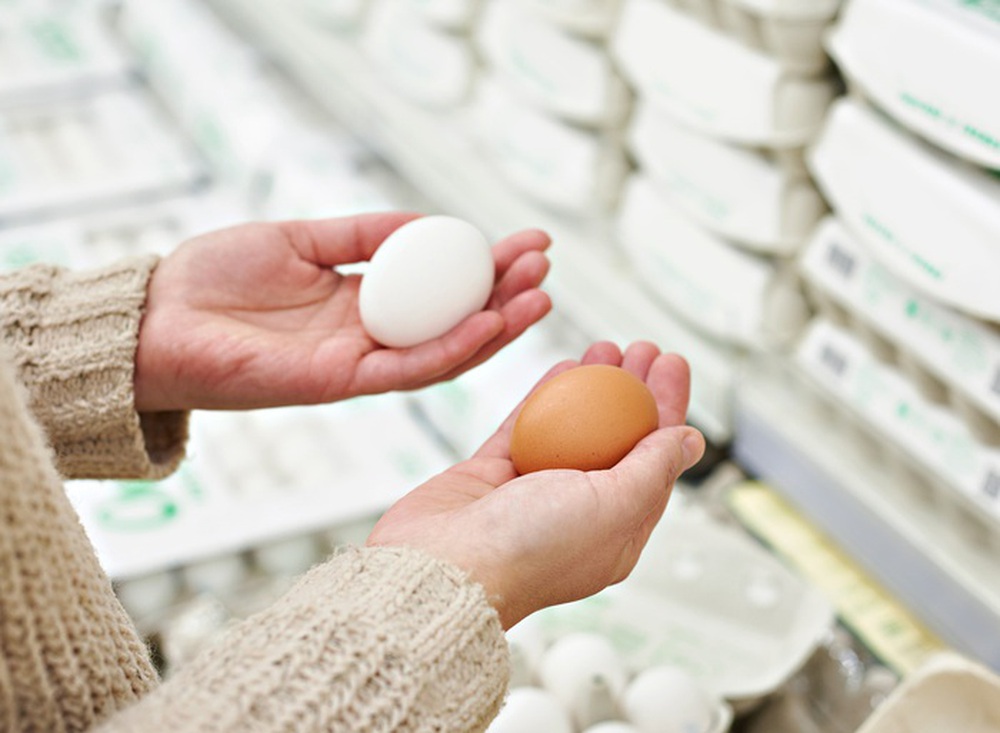

The color of the eggshell does not determine the nutritional value of the egg.
Health benefits of eggs
1. Reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke
A study by Peking University (China) on 4,778 volunteers aged 30-79 found that consuming 4 to 7 eggs per week can help maintain cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
The research team found that people who eat 4 to 7 eggs per week have a relatively high level of ApoA1 (a component of beneficial cholesterol – HDL).
This means that the amount of good cholesterol (HDL) in the body is high, and the level of bad cholesterol (LDL) in the body is lower. This index indicates that eating eggs can help reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.

Research has found that people who eat 4 to 7 eggs per week can help reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. Provides protein
Eggs are one of the protein-rich foods. The protein content in eggs is 13g per 100g of eggs. Protein is an important nutrient that nourishes, builds, and repairs muscle cells. Ensuring an adequate protein intake is significant for human health, and the amino acid composition in eggs is especially good for the body.
3. Improves memory
Choline in lecithin (a fat found in egg yolks) is a necessary nutrient for brain development. Choline is essential for the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that can promote the development of brain cells, activate the nerve transmission function of the brain, improve information processing speed, and enhance memory.

Choline in egg yolks is a necessary nutrient for brain development.
4. Protects vision
Egg yolks contain 2 main antioxidants: lutein and zeaxanthin. These two substances are necessary nutrients for the eyes and can protect light-sensitive cells in our retinas from sunlight and oxidative stress.
5. Good for bones, hair, and nails
Vitamin D in eggs is good for bones and helps prevent diseases such as osteoporosis. In addition, other amino acids, vitamins, and minerals in eggs can help treat biochemical imbalances in the body and improve the health of hair and nails.
According to Vietnamese Women