Some fruits and vegetables can help protect your skin from the sun, but others can make it more sensitive to sunlight and UV rays, activating melanin production and leading to dull, discolored, and rough skin that has lost its elasticity.
But don’t worry, it’s not like you can’t eat these foods at all. You just need to be mindful of how much you eat and when you eat them.
1. Mangoes
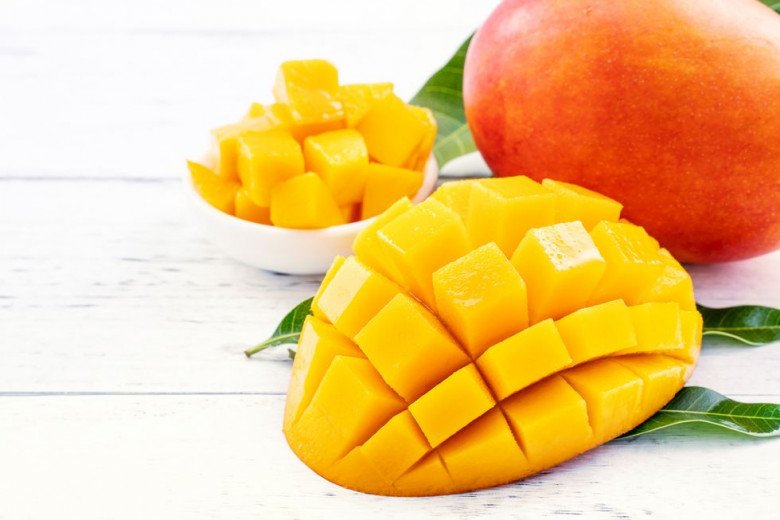

Mangoes are a summer favorite, but they’re also one of those fruits that can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight. However, they are highly nutritious, packed with vitamins A, C, and β-cryptoxanthin.
If you’re concerned about sun exposure, it’s best to enjoy mangoes in the evening. The plant compounds in mangoes can help repair lost neurotransmitters and promote better sleep.
2. Lemons
Lemons are rich in vitamin C and have antioxidant properties that can help brighten the skin. However, consuming lemons after sun exposure can lead to discoloration, so it’s best to enjoy them in the evening.
3. Papayas
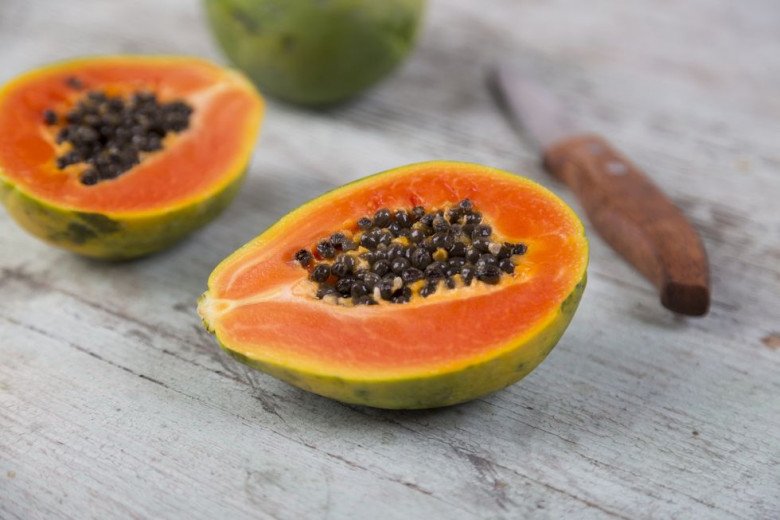

Papayas are an excellent source of potassium, vitamins A and C, and beta-carotene, offering powerful antioxidant benefits. They’re also high in water-soluble fiber, which helps prevent constipation. However, due to their high pigment content, excessive consumption can lead to skin discoloration and carotene xanthesia. So, moderation is key.
4. Jujubes
Jujubes are great for removing free radicals from the body and improving blood vessel health, reducing the risk of heart disease. They’re also high in potassium, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. However, jujubes are sensitive to UV rays, so it’s best to avoid prolonged sun exposure after eating them.
5. Sweet Potatoes
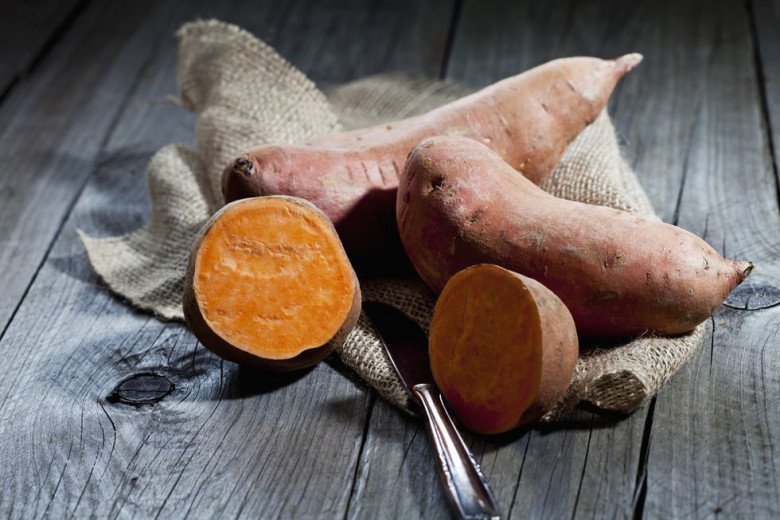

Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of fiber, promoting healthy digestion and reducing constipation. They also aid in detoxification and help prevent colon and rectal cancer. Sweet potatoes are rich in magnesium, potassium, and other minerals, which can reduce edema and maintain stable blood pressure. The vitamin C and carotene in sweet potatoes also have antioxidant effects.
However, due to their copper and other metal content, they can indirectly increase the number and activity of melanin-producing cells in the body. So, during the summer months, when the sun is out for longer periods, remember to enjoy sweet potatoes in moderation.
6. Celery
Celery has a unique aroma and offers a range of health benefits, including improved digestion, lower blood pressure, and reduced edema. It’s rich in vitamins A, C, and K and is a healthy green vegetable. However, because celery also contains potassium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, and other metals, it’s best enjoyed in the evening, and overconsumption can lead to skin discoloration.
7. Carrots
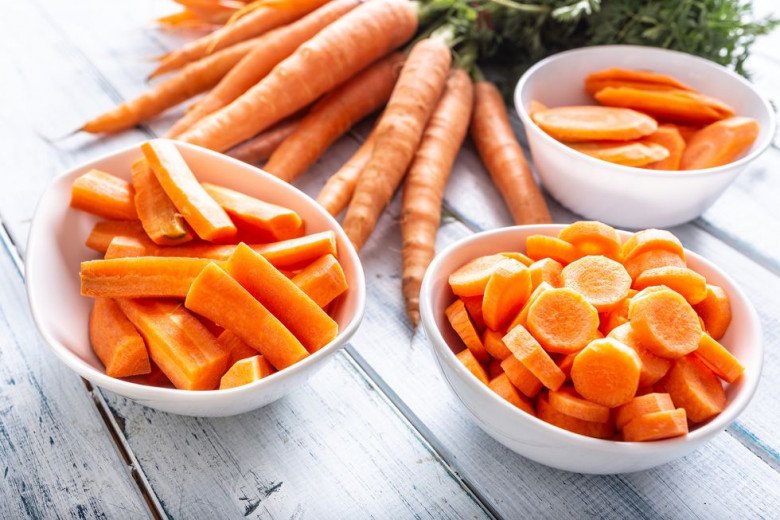

Carrots are well-known for their eye-health benefits and are rich in β-carotene, which aids in cell regeneration and inhibits melanin production. They’re also high in fiber, which is great for weight loss.
However, excessive consumption can lead to skin discoloration and a yellowish hue. If this happens, reduce or stop eating carrots to allow your body to naturally metabolize these pigments.
8. Leeks
Leeks contain volatile oils that can stimulate appetite, improve digestion, lower blood lipids, and reduce blood pressure and arterial hardening. They also inhibit harmful bacteria in the human body. However, leeks are another sun-sensitive food, and consuming them can make melanocytes more active, leading to skin discoloration and pigmentation.
9. Seaweed
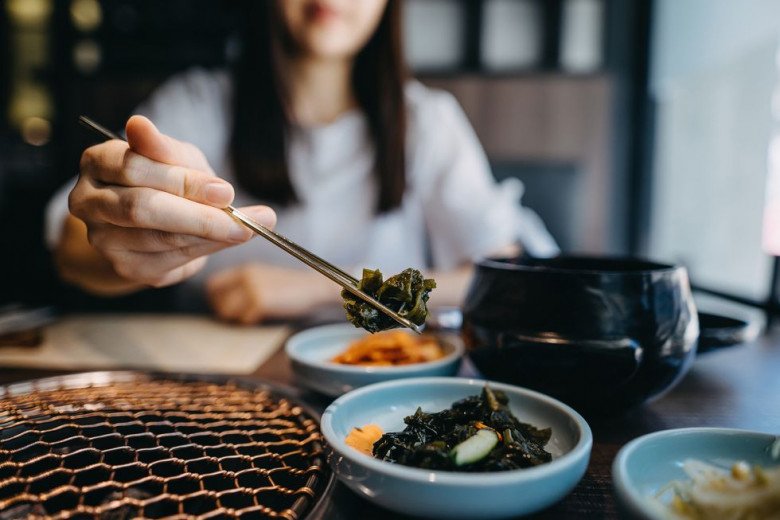

Seaweed is rich in minerals, including iodine, calcium, selenium, and small amounts of iron, cobalt, and arsenic. It’s also very low in fat, so regular consumption is unlikely to lead to obesity.
However, seaweed is sensitive to UV rays and sunlight. Avoid prolonged sun exposure after eating seaweed to protect your skin.
10. Black Sesame Seeds
Black sesame seeds are a great source of essential amino acids and tryptophan, which help relax the brain. They’re also rich in unsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E and have high nutritional value. However, they’re also high in calories and fat and are sun-sensitive, so moderation is important.
The Ever-Blooming Edible Garden: Transform Your Home into a Flourishing Floral Paradise
Are you tired of your dull living space? Do you long for a vibrant, green oasis in your home? This remarkable plant offers the perfect solution. With its ability to provide relaxation, enhance your environment, and even offer a source of fresh, healthy food, it will transform your space into the tranquil haven you’ve always desired.