The liver plays a vital role in the human body, involved in crucial processes such as filtration and detoxification, nutrient metabolism, bile production, and the storage of vitamins and minerals. One of the most serious threats to the liver is cancer, which occurs when changes in the DNA of liver cells lead to uncontrolled growth. These complications can form malignant tumors, causing a myriad of health consequences.
According to Dr. Tran Hai Binh, Deputy Department of Oncology at Tam Anh Hanoi Polyclinic, there are several factors that increase the risk of liver cancer, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and cirrhosis. In addition, lifestyle and habits also contribute significantly to liver cell damage. Maintaining an unhealthy diet, lack of sleep, and physical inactivity can have detrimental effects, increasing the risk of liver cancer.
Eating Moldy Food
Moldy food, especially cereals and nuts such as corn, rice, soybeans, as well as spices, oily seeds, milk, meat, and dried fruit, can produce a dangerous toxin called aflatoxin. Prolonged exposure to aflatoxin can lead to cirrhosis, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
According to Dr. Binh, people working in crop and moldy food processing are at high risk of exposure to this toxin, especially when they frequently inhale dust from their work environment. The danger is even greater for those already infected with chronic hepatitis B or C, making them more susceptible to aflatoxin-induced liver cancer.
To protect your health, Dr. Binh emphasizes that consumers should absolutely avoid moldy food. Even partially moldy food should be discarded, as mold can spread to parts that are not visible to the naked eye. Before preparing dry foods such as cereals, beans, and peanuts, it is important to carefully inspect for signs of mold, unusual odors, or color changes.
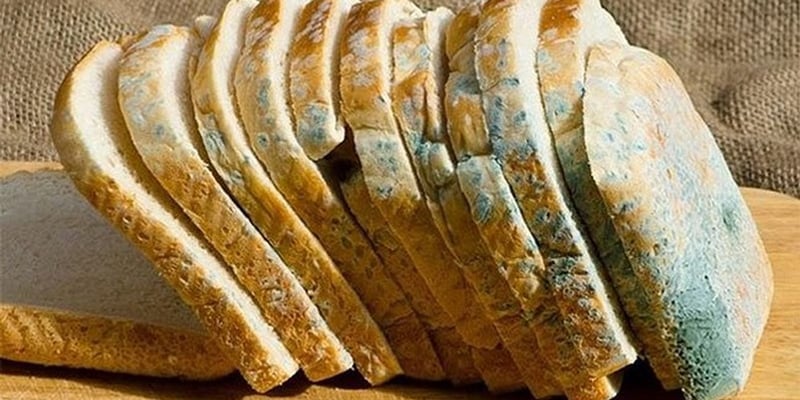

Carefully inspect dry foods such as cereals, beans, and peanuts for signs of mold, unusual odors, or color changes before preparation
A Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is becoming a leading cause of weight gain and obesity. These conditions not only bring about a host of health issues but also increase the risk of serious diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. When excess fat accumulates in the liver, it can lead to more dangerous complications such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer.
To protect liver health, adults need to maintain a reasonable body weight through physical activity. Exercises such as walking, running, cycling, or swimming help burn excess fat and reduce the risk of fat accumulation in the liver. Adopting a regular exercise regimen is essential to improve overall health and prevent liver-related diseases.

Maintain a healthy weight through physical activity to protect your liver
Consuming Highly Processed Food
The frequent consumption of highly processed food, such as fast food, canned goods, bacon, sausages, and industrial confectionery, can be extremely detrimental to health. These products often contain high levels of additives, preservatives, salt, sugar, and saturated fat, all of which can negatively impact the liver and increase the risk of cancer.
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), certain food additives such as nitrites and nitrates, commonly found in processed meats like sausages and bacon, are identified as probable carcinogens, particularly for liver cancer.
Nutrition experts advise that instead of relying on processed food, individuals should focus on a healthy diet comprising plenty of green vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats. Additionally, limiting sugar intake and reducing the consumption of processed products not only improves overall health but also reduces the burden on the liver, helping to prevent serious diseases in the future.

Adopt a healthy diet with an abundance of green vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Regular and excessive alcohol consumption overworks the liver, as it has to continuously process and detoxify these substances. The constant overload leads to severe liver damage, paving the way for a range of liver diseases such as hepatitis, fatty liver, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Especially for those with chronic hepatitis B or C, combining alcohol with these conditions greatly increases the risk of liver cancer.
Experts recommend limiting or completely abstaining from alcohol, especially for those with existing liver issues. For individuals with a history of long-term alcohol consumption, it is crucial to undergo regular liver function tests every 6 to 12 months. This helps detect any abnormalities early on, allowing for timely intervention to protect liver health.