## Water Spinach’s Nutritional Value
Water Spinach’s Nutritional Value
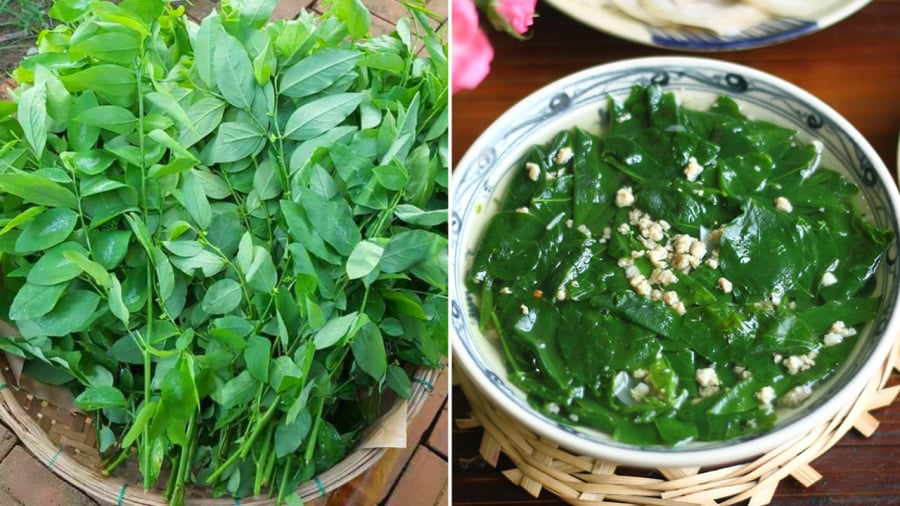
Water spinach, known as “rau ngót” in Vietnamese, is a nutrient-rich vegetable that is widely accessible. You can easily find this vegetable at local markets or supermarkets. Water spinach boasts an impressive array of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A and C, fiber, plant-based protein, and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Notably, water spinach is an excellent source of vitamin C, even surpassing the levels found in many other vegetables. Vitamin C boosts immunity, acts as an antioxidant, and promotes healthy skin. Additionally, the vegetable contains vitamin A, beneficial for vision and skin health. The fiber content in water spinach improves digestion and helps prevent constipation. It is also a good source of iron and calcium, which prevent anemia and support bone health. A 100-gram serving provides 2.7 grams of beneficial plant-based protein.
Furthermore, water spinach contains anti-inflammatory substances such as glucosinolate and flavonoid, which protect the body against chronic diseases. Traditional beliefs hold that water spinach has detoxifying properties and can promote lactation in postpartum women.
Who Should Avoid Water Spinach
While water spinach offers a plethora of nutrients, it may not be suitable for everyone. Certain individuals should limit or avoid consuming this vegetable to maintain their health.
-
Pregnant women, especially during the first trimester
Although water spinach is beneficial for postpartum women, it is not recommended for pregnant women, particularly during the initial three months of pregnancy. Water spinach contains papaverine, a substance that can induce uterine contractions, increasing the risk of miscarriage or preterm labor. While the levels of papaverine in water spinach are not extremely high, pregnant women, especially in their first trimester, should exercise caution. It is crucial to avoid consuming raw water spinach during pregnancy. If consumed, it should be cooked thoroughly and eaten in moderate quantities.

- Individuals with kidney stones or a family history of kidney stones
Water spinach contains significant amounts of calcium oxalate, which can increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Therefore, individuals who have experienced kidney stones or have a family history of the condition should limit their consumption of water spinach. If consumed, it is essential to cook it thoroughly, use minimal salt, and ensure adequate hydration to prevent oxalate buildup in the body.
- People with calcium deficiency or osteoporosis
While water spinach provides calcium, it is also rich in oxalic acid, which can hinder calcium and mineral absorption in the body. Thus, individuals with calcium deficiency or osteoporosis should limit their intake of water spinach, especially in its raw form.
- Individuals with insomnia or sleep difficulties
Water spinach contains glucosinolate, which stimulates the nervous system and may make it challenging to relax. Therefore, consuming water spinach close to bedtime can potentially disrupt sleep, especially for those with sensitive constitutions.
- Individuals taking certain medications
Water spinach may interact with specific medications, particularly those related to the nervous system or diabetes treatment. The presence of papaverine and other compounds in water spinach could reduce the effectiveness of these medications.
Precautions When Consuming Water Spinach
While water spinach is nutritious, it should not be consumed excessively. It is advisable to avoid eating raw water spinach. Cooking it thoroughly before consumption is recommended. High temperatures reduce the levels of papaverine and oxalic acid, which could otherwise be detrimental to health. It is suggested to limit water spinach consumption to 2-3 times per week, with each serving ranging from 50 to 100 grams.
In conclusion, while water spinach offers numerous health benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone. This article identifies five groups of individuals who should exercise caution when consuming water spinach to ensure they reap the vegetable’s advantages while avoiding any potential adverse effects.
The Ultimate Superfood Fish: A Delicious, Nutritious Catch with a Surprising Twist
Anchovies are a humble yet beloved fish species commonly found in Vietnam. Beyond their use in producing fish sauce, these small, oily fish are transformed into a variety of delectable dishes. From crispy fried anchovies to savory stews and soups, these versatile fish offer a range of flavors and textures that have captured the hearts (and taste buds) of many.