As summer arrives, Vietnam’s fruit markets come alive with a plethora of unique fruits such as lychees, plums, and jackfruit. However, many people are hesitant to indulge in these treats due to concerns about their heating properties, believing that they can cause acne, mouth ulcers, and even itching and discomfort. But is there any truth to these claims? Let’s explore this topic from a nutritional perspective to gain a clearer understanding.
What does “heating property” refer to?
The concept of “heating property” is not recognized in modern medicine, but it is a common belief in everyday life. Typical symptoms associated with this condition include acne, mouth ulcers, itching, frequent urination, constipation, and a feeling of restlessness.
While there is no official scientific definition, many nutrition experts attribute these symptoms to an imbalanced diet, excess energy intake, dehydration, or insufficient fiber consumption.
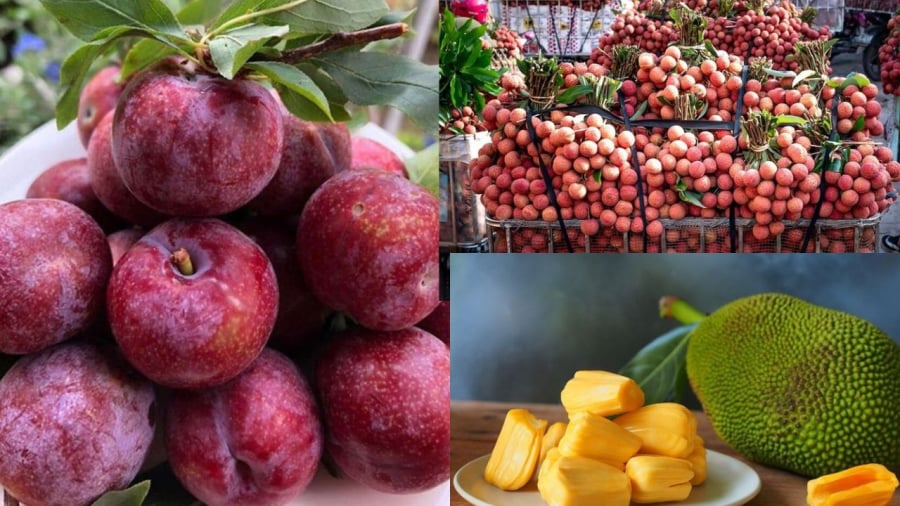

Do lychees have heating properties?
Nutritional value of lychees: Lychees (Litchi) are tropical fruits packed with vitamin C, potassium, antioxidants, and natural sugars. On average, 100g of lychees contain approximately 66 kcal and nearly 15g of sugar. They boost immunity, improve blood circulation, and promote healthy skin.
Why are lychees considered heating?
Lychees are high in sugars (fructose and glucose), and consuming excessive amounts can lead to a sudden spike in blood sugar levels, resulting in energy imbalance and symptoms such as hot flashes, acne, and a feeling of restlessness. The National Institute of Nutrition recommends that adults consume only 5-10 lychees per day, depending on their body constitution.
Note: Children who consume too many lychees, especially on an empty stomach, may experience hypoglycemia due to metabolic disorders, as observed in certain lychee-growing regions like India.
Do plums have heating properties?
Nutritional content of plums: Plums from Hanoi or northern Vietnam (Prunus salicina) are rich in vitamins A and C, fiber, and antioxidants such as polyphenols and anthocyanins, which have anti-inflammatory properties and support digestion and immunity.

Is it true that plums have heating properties?
Contrary to folk belief, plums do not possess heating properties and can even help with mild liver detoxification and bowel movement. However, consuming large quantities of plums (more than 300g per day) may lead to increased stomach acid, causing a burning sensation, discomfort, or mild acne due to high fructose content. Some individuals with sensitive constitutions may also experience acne breakouts.
In summary: Plums do not cause heating if consumed in moderate amounts. It is recommended to eat the skin to benefit from the antioxidants and avoid excessive salt or spicy chili dips to minimize gastric irritation.
Does jackfruit cause acne or a heating sensation?
Nutritional profile of jackfruit: Jackfruit is a good source of carbohydrates, vitamins C and B6, magnesium, potassium, and plant compounds like lignans and saponins, which have anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties.
100g of jackfruit provides approximately 95 kcal, which is relatively high compared to other fruits, and it contains a significant amount of natural sugars. Therefore, overeating jackfruit can easily lead to excess energy intake.

Does jackfruit have heating properties?
Jackfruit is often labeled as heating due to the consequences of overconsumption: bloating, indigestion, acne, or constipation if not adequately hydrated. However, when consumed in moderate amounts (100-200g per day) and paired with sufficient water intake, jackfruit is a nutritious food.
Suggestion: Consider pairing jackfruit with unsweetened yogurt or consuming it 30 minutes after a main meal to aid digestion.
How should we eat these fruits to avoid their heating properties?
- Eat a diverse and moderate amount of fruits: Avoid overeating any single type of fruit, whether it be lychees, plums, or jackfruit. Alternate between different fruits, and aim for a total daily intake of 200-300g of fresh fruit.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration in the summer can exacerbate the symptoms of “heating property.” Aim for a daily water intake of 1.5-2 liters.
- Increase your intake of cooling foods: Include cooling foods such as pennywort, water spinach, winter melon, and dragon fruit to help regulate your body’s temperature.
- For those with heat-prone constitutions or acne-prone skin, avoid eating fruits on an empty stomach or combining them with spicy, hot foods (salty chili dips, fried foods, etc.).
- Individuals with high blood pressure or diabetes should monitor their consumption of sweet fruits like jackfruit and lychees, as they can elevate blood sugar levels.
Lychees, plums, and jackfruit do not inherently possess heating properties when consumed in appropriate amounts and ways. The perception of heating is largely attributed to improper eating habits, such as overeating, consuming fruits on an empty stomach, dehydration, imbalanced diets, or individual sensitivities. Instead of abstaining from these delicious summer fruits, embrace them in a balanced and informed manner to maintain your health and enjoy their natural goodness.