Longevity is not just a matter of genetic luck, but also a reflection of one’s healthcare practices. While no one can accurately predict how long a person will live, paying attention to your body, especially the lower half, can give some insights into longevity. Here are three common characteristics of long-living, healthy individuals.
1. Resilient Knee Joints – The Foundation of Longevity
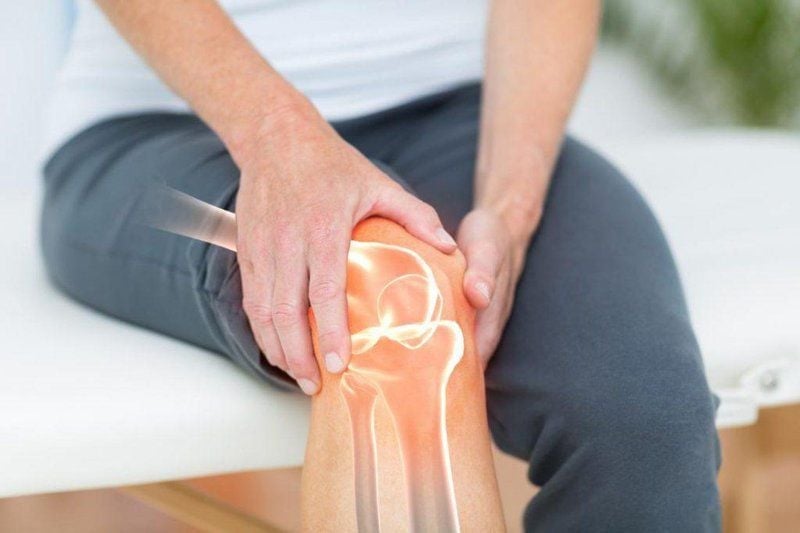
It’s no surprise, then, that those with healthy knee joints tend to live longer. Just imagine: without flexible knees, basic activities like walking, running, climbing stairs, or playing sports would be challenging. For older adults, being able to move around comfortably indicates good bone and muscle health, stable blood circulation, and a high capacity for self-care. On the other hand, if you’re younger and already experiencing knee pain, inflammation, or fluid accumulation, consider it an early warning sign about your overall health. Maintaining resilient and strong knee joints not only preserves your mobility but also contributes to a longer life expectancy.
2. Steady Feet – A Sign of Healthy Circulation and Nervous System
Feet are not just for moving around; they are also home to a network of blood vessels, nerves, and major muscle groups. For older individuals, maintaining balance, walking naturally, and having intact sensation in the feet are vital indicators of an efficient circulatory and nervous system. Smooth blood flow in the legs ensures that oxygen and nutrients reach the organs more effectively, reducing the risk of stroke, heart disease, and metabolic disorders. Healthy nerves in the feet enable quick reflexes, preventing falls—a leading danger for the elderly. Well-toned leg muscles ensure mobility is preserved for longer, enhancing overall quality of life. Conversely, muscle atrophy, poor circulation, or numbness in the legs signal rapid physical decline.
3. Robust Pelvic Organs – The Unsung Guardians of Health
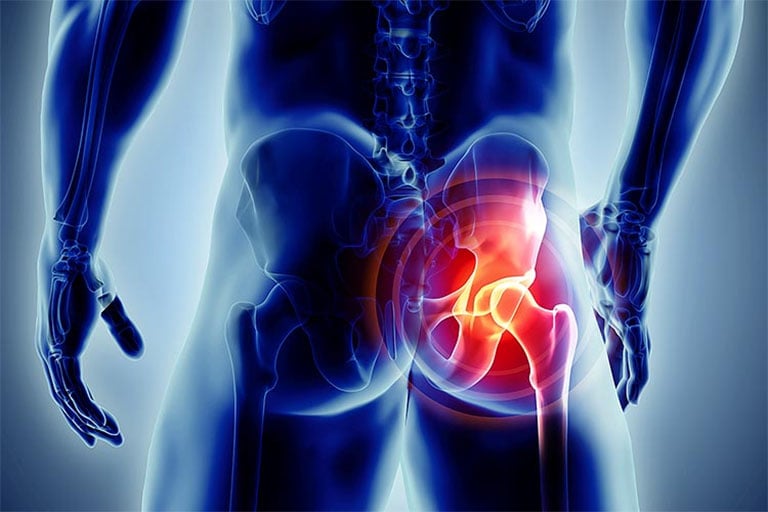
In men, the prostate, bladder, and rectum are essential, while in women, it’s the ovaries, uterus, bladder, and rectum. These organs are at high risk of age-related damage but are often overlooked during routine check-ups. Weakness or injury in the pelvic region not only impacts quality of life regarding urination, digestion, and sexual function but also increases the likelihood of severe conditions like prostate, ovarian, uterine, bladder, or rectal cancer. Therefore, long-living individuals tend to maintain stable pelvic health, undergo regular check-ups, and lead moderate and hygienic lifestyles.
Longevity is not solely dependent on chance; it reflects how one treats their body. A robust body, from the knees to the feet and pelvic region, is the foundation for a long and fulfilling life. Don’t wait until old age to start caring; invest in the health of your lower body starting today—after all, taking care of your health is an investment that never disappoints.
What is the Feng Shui Significance of the Mulberry Tree? Unraveling the Ancient Wisdom Behind Planting Mulberry Trees Alongside Cycas and Money Plants.
The ficus tree, also known as the “tree of life”, has long been revered in Asian cultures for its symbolic significance and aesthetic beauty. It is believed that keeping a ficus tree indoors brings good fortune and prosperity, making it a popular choice for those who practice feng shui. Traditionally, the ficus tree is often accompanied by two other plants, the Cycas revoluta and the Fukien tea tree, forming a trio known as the “Three Gods of Longevity”. This harmonious combination is thought to bring balance and harmony to the home, as well as enhance the flow of positive energy.