In a recent article published by Sohu, Dr. Zhang, an experienced physician specializing in cancer treatment, particularly stomach cancer, shared his insights on a troubling question he often receives: “Why did my family develop stomach cancer when we avoided salty and oily foods and maintained a healthy lifestyle?”
According to Dr. Zhang, the primary culprit lies in improper food storage practices. He emphasizes, “Through my years of working directly with patients, I’ve uncovered a concerning health issue. Storing food in the refrigerator for extended periods, an action that may seem harmless, can actually be a risk factor for stomach cancer.”
Overnight Stored Soup
Dr. Zhang recounts the case of a middle-aged female patient who presented with typical stomach ailments, including nausea, loss of appetite, and indigestion. Initially, she attributed these symptoms to common stomach inflammation and didn’t seek immediate medical attention. However, as the abdominal pain intensified, she decided to visit the hospital. Examinations revealed severe inflammation and ulceration in her stomach, with even signs of pre-cancerous changes.
Upon investigating the patient’s dietary habits, Dr. Zhang discovered that she routinely cooked a large pot of soup, stored it in the refrigerator, and reheated it for subsequent meals. She believed that refrigerating the soup would prevent it from spoiling. Unfortunately, this convenient practice turned out to be the root cause of her severe health issue.
When the soup is repeatedly heated and cooled, its nutritional components, such as proteins and fats, undergo oxidation. This process generates harmful compounds, notably nitrites, which can transform into nitrosamines in the body. Nitrosamines are well-known for their cancer-causing potential and can irritate the stomach lining, increasing the risk of stomach cancer.
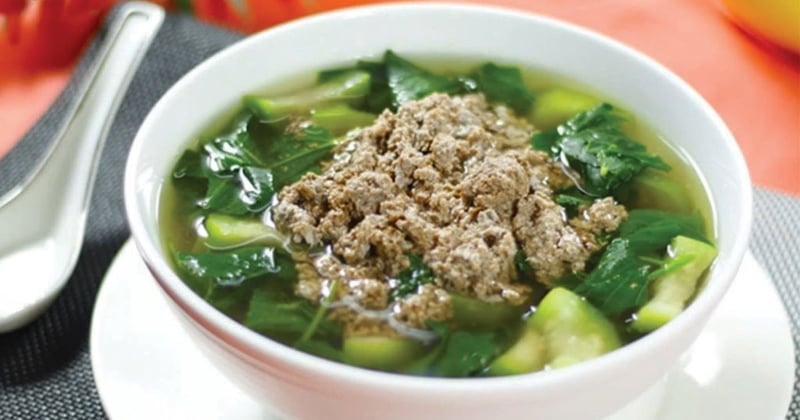

The repeated heating and cooling of the soup cause oxidation of proteins and fats
Long-Term Storage of Seafood
Seafood is naturally rich in protein and essential micronutrients. However, improper storage can turn it into a breeding ground for bacteria. Some of these bacteria not only cause harm but also produce toxins, increasing the risk of food poisoning.
Additionally, when seafood is stored for extended periods, it can generate histamine, a natural compound that does not directly cause cancer. However, when combined with certain bacteria, histamine can transform into harmful substances, potentially increasing the risk of cancer.
Dr. Zhang treated a male patient in his 50s who worked in aquaculture and often brought home fresh seafood, storing it in the refrigerator for gradual consumption over several days. This practice continued for years until he started experiencing severe stomach pain. Examinations revealed severe stomach inflammation and eventual diagnosis of stomach cancer.
The primary cause was attributed to the long-term storage of seafood, especially when not promptly cooked and consumed. This allowed bacteria to break down the seafood, producing nitrosamines, which are closely linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer.
Moldy Food
A 60-year-old retired female teacher suffered from prolonged stomach aches for years. Initially, she disregarded these symptoms as minor and non-threatening. However, as the discomfort intensified and began affecting her daily life, she decided to seek medical attention.
Examinations revealed severe damage to her stomach lining due to chronic inflammation. Interestingly, her dietary habits and food storage practices played a significant role in this condition. She often left leftovers, such as cold rice, ready-to-eat meals, and other foods, in the refrigerator for weeks, sometimes even months.
While she believed that refrigeration kept the food fresh and safe, the truth is that low temperatures only slow down spoilage; they do not entirely prevent bacterial or mold growth. Foods with high moisture content, like rice, bread, and vegetables, are particularly susceptible to mold development. Even when the food appears normal, it may still contain mycotoxins—harmful substances that can severely affect stomach health and overall well-being.
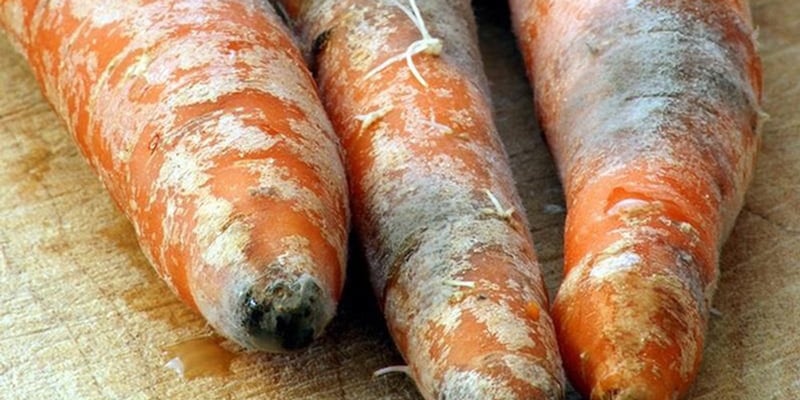

High-moisture foods like rice, bread, and vegetables are prone to mold development
Long-Term Storage of Condiments
Condiments such as soy sauce, vinegar, salt, and dipping sauces are kitchen staples. However, few people realize that prolonged refrigeration can alter their quality and turn them into health hazards.
A young male patient working in the culinary industry was diagnosed with severe stomach inflammation and pre-cancerous gastric ulcers during a routine health check-up. Upon investigating his dietary and food storage habits, Dr. Zhang discovered that he tended to stockpile condiments, especially soy sauces and salty sauces, in his refrigerator.
When stored for extended periods, these condiments can increase their nitrite content. When combined with amino acids from food, nitrites can transform into nitrosamines, known for their cancer-causing potential. This was a contributing factor to the patient’s severe stomach inflammation.
Based on these cases, Dr. Zhang emphasizes the importance of adhering to basic food storage guidelines to minimize the risk of stomach cancer associated with refrigerator usage. These guidelines include:
– Regularly cleaning the refrigerator: Avoid letting food linger for too long, especially fresh produce and ready-to-eat meals.
– Limiting food reheating: If there is leftover soup, store it for no more than 24 hours and ensure proper reheating before consumption.
– Consuming seafood as soon as possible: Avoid long-term storage to prevent the formation of harmful toxins.
– Checking for signs of spoilage: Even if food appears normal, pay attention to expiration dates, unusual odors, and discoloration before consuming.
– Discarding expired or altered condiments: If condiments show signs of discoloration, strange odors, or visible deterioration, throw them out instead of using them.
These seemingly simple habits play a crucial role in safeguarding our health, especially in preventing digestive issues such as stomach inflammation and reducing the risk of stomach cancer.