According to
Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, including about 70 known carcinogens such as benzene, formaldehyde, and nitrosamines. These substances damage lung cells and lead to genetic mutations, increasing the risk of cancer.
In addition, exposure to toxic chemicals such as asbestos, arsenic, radon gas, along with air pollution and radiation, contribute to the increased risk of developing lung cancer. In terms of endogenous causes, genetic mutations such as EGFR, KRAS, and ALK can lead to abnormal cell growth and cancer.
Apart from the above factors, age (especially over 50), a history of lung disease such as COPD or tuberculosis, genetic factors (a family history of lung cancer), and a weakened immune system are important reasons for the increased likelihood of developing lung cancer.
“Notably, lung cancer is also associated with dietary habits. Several studies indicate that a diet lacking in green vegetables and high in red meat, coupled with living in an environment polluted with smoke and dust, are contributing factors to the disease,” says Dr. Phuong.
What are the warning signs of lung cancer?
Early detection is key to improving survival rates for lung cancer patients.
One of the most overlooked signs is a persistent cough, a common symptom in various respiratory conditions. However, Dr. Phuong warns that if you experience a prolonged cough, especially if it produces blood, along with any of the following symptoms, it should not be ignored:
Cough lasting continuously for more than two weeks without a clear cause.
Coughing up blood, chest pain or tightness, difficulty breathing, or hoarseness.
Unexplained weight loss and prolonged fatigue.
In advanced stages: bone pain, headaches (due to brain metastases), facial or neck swelling.
Early detection of lung cancer, when the tumor is still small and has not spread (stage I), can significantly improve the chances of survival. The five-year survival rate in such cases can be as high as 90%. However, if the cancer is detected at a later stage (stages III-IV), this rate drops drastically to less than 20%.
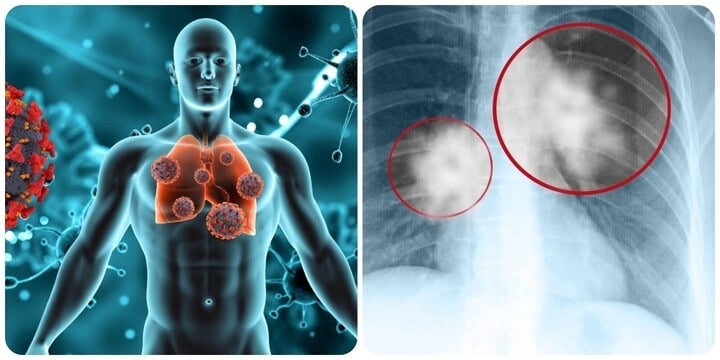
Regular screening is the best protection
Dr. Phuong recommends that long-term smokers (over 20 years) undergo low-dose chest CT screening. This method can detect very small lesions, as small as 2-3mm, and reduces radiation exposure by up to 20% compared to conventional CT scans.
Additionally, those with a high risk, such as a family history of lung cancer, occupational exposure to asbestos or radon, or a history of chronic lung disease, should consider starting screening from the age of 40.
Prevention is better than cure
To reduce the risk of lung cancer, individuals should:
Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
Minimize exposure to air pollutants and toxic chemicals.
In polluted environments, wear protective masks to safeguard respiratory health.
Adopt a nutrient-rich diet with an emphasis on cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli and kale), and foods high in vitamins C and E.
Engage in regular physical activity for at least 30 minutes daily to boost immunity.
7 Warning Signs of Cancer: Why You Must Not Ignore These Symptoms
“It is imperative to be vigilant about your health and seek medical attention when symptoms arise. Unfortunately, many patients only present with clear symptoms in the middle or later stages of their condition. To ensure early detection, be mindful of these seven crucial signs and symptoms that could indicate a serious health issue.”