Common Types of Blood Cancer
1. Leukemia (approximately 36%)
According to Dr. Ha Hai Nam, Deputy Head of the Department of Abdominal Surgery I at K Tan Trieu Hospital in Hanoi, acute leukemia occurs when the body produces an excessive amount of immature white blood cells.
These cells clog the bone marrow and hinder the production of normal blood cells such as red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which aid in blood clotting), leading to immune disorders and a higher susceptibility to other diseases. Leukemia is also known as “white blood.”
2. Lymphoma (lymphoma – about 46%)
Lymphocytes are present in almost all organs of the body, especially in the lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. When lymphocytes proliferate abnormally, they cause the lymph nodes to swell and may spread, affecting the entire body.
3. Myeloma (about 18%)
Myeloma is a disorder of plasma cells (plasmacytes) in the bone marrow—the type of cell that produces antibodies to fight infections. When these plasmacytes become dysregulated and grow uncontrollably, they produce abnormal antibodies, leading to osteoporosis, bone fractures, kidney failure, anemia, immune deficiency, hypercalcemia, and even neurological symptoms and severe infections.
Blood Cancer Symptoms That Are Easily Overlooked
Blood cancer is a dangerous disease that progresses insidiously with many vague manifestations, causing patients to be complacent. The following are common symptoms that, according to Dr. Ha Hai Nam, Deputy Head of the Department of Abdominal Surgery I at K Tan Trieu Hospital, many people often do not notice:
1. Digestive Symptoms
When cancer cells accumulate in the liver, kidneys, spleen, or intestines, the body may exhibit the following symptoms:
Persistent or intermittent abdominal pain
Loss of appetite or decreased appetite
Prolonged nausea and indigestion
2. Blood Clotting Disorders
Due to the decrease in platelets, patients may experience the following:
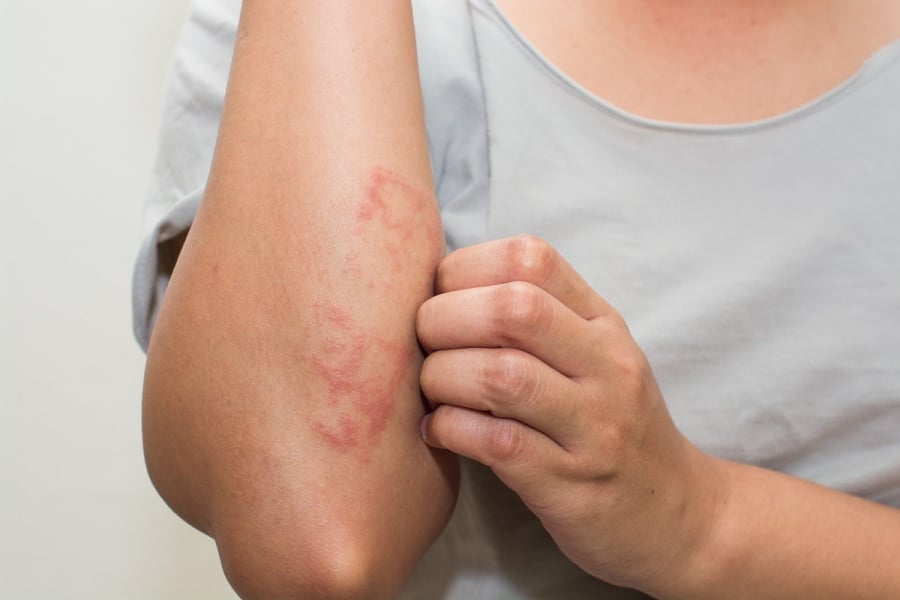
Bruising on the skin without an apparent cause
Prolonged gum bleeding or nosebleeds
Tiny hemorrhagic spots on the skin or mucous membranes
Wounds that are difficult to stop bleeding
3. Signs of Oxygen Deficiency in the Blood
The reduction in red blood cells causes oxygen deficiency, leading to the following symptoms:
Prolonged fatigue and exhaustion, even with rest
Unexplained weight loss
Shortness of breath, chest pain, and frequent headaches
4. Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Blood cancer can also affect the musculoskeletal system:
Bone and joint pain in multiple locations, such as the legs, back, and shoulders
Bone fractures without apparent trauma
5. Prolonged Infections
A weakened immune system makes individuals more susceptible to infections:
Fever of unknown origin, along with prolonged chills
Night sweats
Slow-healing wounds that are prone to reinfection
Skin rashes or itching without an apparent cause
6. Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin—they can be felt but are usually painless and unresponsive to medication.
Deep-seated lymph nodes, such as those in the abdominal cavity or chest, can cause abdominal pain, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
According to the American Cancer Society, blood cancer accounts for about 10% of all cancer cases diagnosed annually in the United States, with over 175,000 new cases each year.
While treatment is often lengthy and expensive, early detection can lead to a success rate of over 90%. Therefore, if you experience any of the aforementioned abnormal symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.