Fats and oils are essential components of a healthy diet, providing essential fatty acids that aid in the absorption of vital vitamins and minerals such as vitamins A, B, D, and E, as well as calcium. A deficiency in these healthy fats can lead to malnutrition and impaired development, especially in children.
In the past, during times of economic hardship, pork fat was considered a valuable food source.
With the introduction of vegetable oils into the market, concerns arose about the high cholesterol content in pork fat and its potential negative impact on health. However, this information is not entirely accurate, and there are benefits to consuming pork fat in moderation.
The Great Debate: Pork Fat vs. Vegetable Oil – Uncovering the Truth
Pork fat is a rich source of vitamin D and minerals, playing a crucial role in calcium absorption and nerve function. It also enhances the absorption of vitamin A, something vegetable oils cannot offer. Additionally, pork fat contains saturated fatty acids that are stable at high temperatures, contributing to the Maillard reaction during cooking, which gives food a delightful flavor and aroma.
On the other hand, excessive consumption of pork fat can lead to increased cholesterol levels and, over time, contribute to atherosclerosis. For this reason, individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, or high blood cholesterol, should consume pork fat in moderation.
Vegetable oils, while providing similar energy content to pork fat, have lower levels of “bad” cholesterol and are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, which aid in cholesterol metabolism. This makes them a heart-healthy choice and beneficial for preventing cardiovascular disease and hypertension.
However, a drawback of vegetable oils is their susceptibility to oxidation when exposed to high temperatures. This can lead to the formation of harmful compounds, altering the oil’s nutritional profile. Therefore, it is essential to use oils within their smoke points and not subject them to excessive heat.
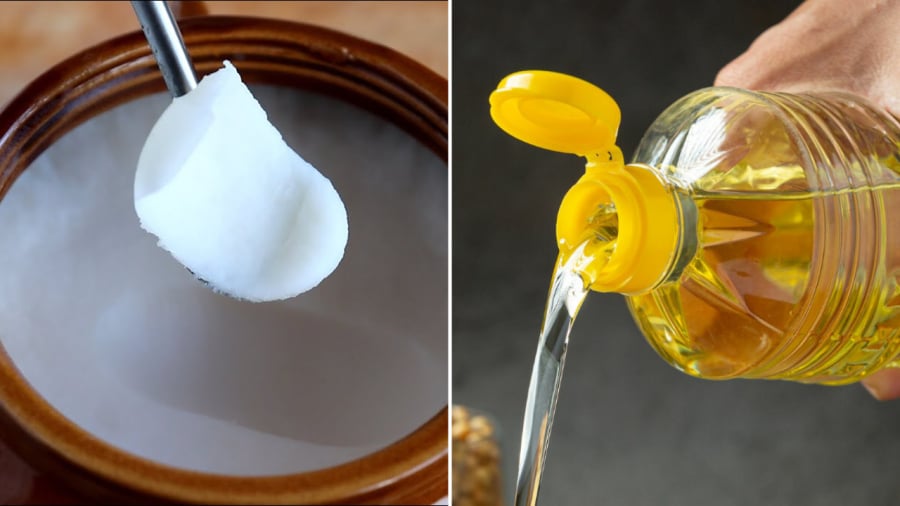

A balanced approach to healthy eating is to incorporate both pork fat and vegetable oils into your diet. According to the National Institute of Nutrition, the ideal ratio of pork fat to vegetable oil for adults is 50:50. For infants under one year old, a ratio of 30:70 is recommended, gradually increasing to 50:50 for children over one year of age.
Tips for Using Pork Fat and Vegetable Oil in Your Diet
Pork fat is more stable at high temperatures and can be used for frying and sautéing, ideally within a temperature range of 120-180°C. For low-heat cooking methods, such as stir-frying and making salad dressings, vegetable oils are a better choice.
It is best to avoid reusing frying oils and fats multiple times, as this can lead to the formation of harmful compounds and an increase in cholesterol levels. Reusing cooking oils and fats can also introduce toxins into your food, which may have negative health effects.
In conclusion, rather than exclusively relying on either pork fat or vegetable oil, a varied and balanced approach that incorporates both can ensure you receive the full range of nutritional benefits that each has to offer.
The Magic Brew: A Daily Cup to Lower Cholesterol.
Introducing a traditional herbal drink with a twist – a potent concoction that offers a plethora of health benefits, especially for those seeking to trim down and tone up. This magical brew is a game-changer for those eager to shed some pounds and achieve their dream physique. Discover the secrets of this ancient remedy, now revamped for the modern health enthusiast.