People with shorter life expectancies often exhibit the following 3 excesses and 2 deficiencies:
2 Excesses Commonly Found in People with Shorter Life Spans
1. Excess Belly Fat
Research suggests that adults with larger waist circumferences have a higher risk of premature death compared to those with normal waist sizes.
A larger waist circumference leads to abdominal obesity, which is associated with conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, high blood pressure, and coronary artery disease.
The United States enjoys one of the highest standards of living and medical care in the world, yet its average life expectancy is only 78 years.

In contrast, Japan, despite having a less advanced economy and society, boasts a life expectancy of 84 years. This six-year difference is significant.
One of the main reasons for this disparity is attributed to the high obesity rates in the US. The American fondness for fried and sugary foods has resulted in obesity rates reaching 30%.
Obesity often brings a host of health issues, impacting the liver, pancreas, digestive system, and numerous other organs.
2. Excess Energy from Dinner
Some medical experts believe that 25% of the function of dinner is to sustain life, while the remaining 75% increases the risk of ending up in the hospital.
In Vietnamese culture, dinner is an important meal, and many are accustomed to eating delicious and abundant food in the evening. Social gatherings and celebrations often take place at night as well.
However, overeating at dinner can be detrimental to health. Excess calories not only lead to obesity but also place a strain on the digestive system and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
It is recommended to have a lighter dinner, reducing consumption of red meats like pork, beef, and lamb, and increasing intake of vegetables, whole grains, fish, seafood, and other low-fat foods.
3 Deficiencies That Harm Health
1. Lack of Laughter
According to a study by Wayne State University in the US, people who laugh frequently tend to live about seven years longer than those who laugh infrequently.
Why does such a simple facial expression make such a significant difference in lifespan? Researchers offer two main reasons.
First, laughter can reduce adrenaline levels, benefiting heart rate stability, reducing fatigue, and regulating blood pressure.
Second, people who laugh often tend to have positive and optimistic personalities, exhibiting extroverted traits and being less susceptible to mental health issues.
So, if you want to live longer, combine a healthy diet with more laughter. A generous and carefree attitude will contribute to longevity.
2. Lack of Physical Activity (Less Than 3 Hours/Day)
With advancements in science and technology, most modern jobs can be done from the comfort of an office. Consequently, people are sitting more and moving less.
As early as 2003, the World Health Organization pointed out that approximately two million deaths worldwide each year were associated with physical inactivity. By 2020, it was estimated that 70% of health problems could be traced back to sedentary lifestyles.
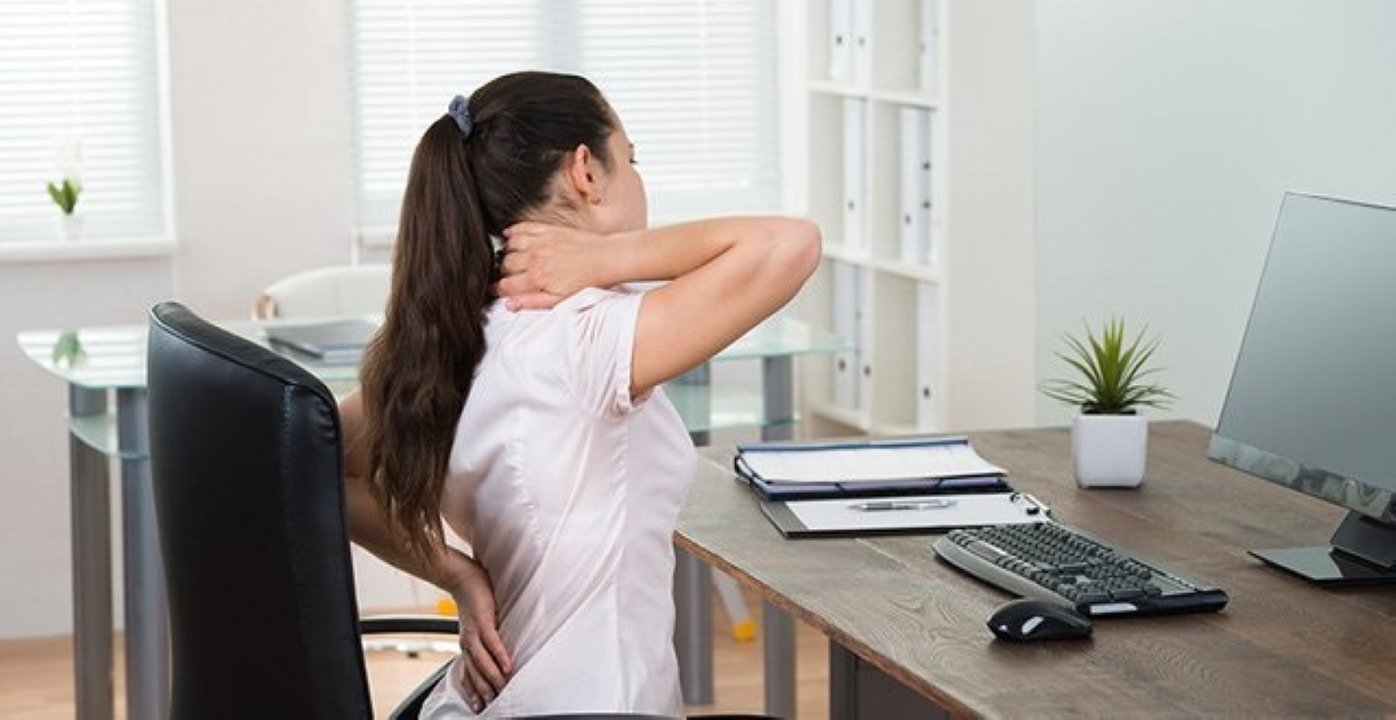

When sitting for extended periods, the lumbar spine and cervical spine endure prolonged stress, which can cause damage. Maintaining the same posture also hinders blood circulation, impacting vital organs and tissues such as the heart, brain, and blood vessels.
Additionally, inactivity slows digestive motility and reduces digestive secretions, negatively affecting digestive health.
To counteract the harmful effects of a sedentary lifestyle, it is recommended to avoid sitting for more than three consecutive hours. Ideally, take a break every hour to stand up, stretch, and engage in light physical activity for 5–10 minutes.
3. Lack of Positivity
Psychology plays a crucial role in longevity. It is understood that a pessimistic, negative, and depressed person is more likely to develop unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol abuse, sleep deprivation, and irregular eating patterns.
Moreover, individuals with negative mindsets are more susceptible to external influences. When faced with challenges and obstacles, they allow negative emotions to overwhelm them, causing significant harm to their bodies.