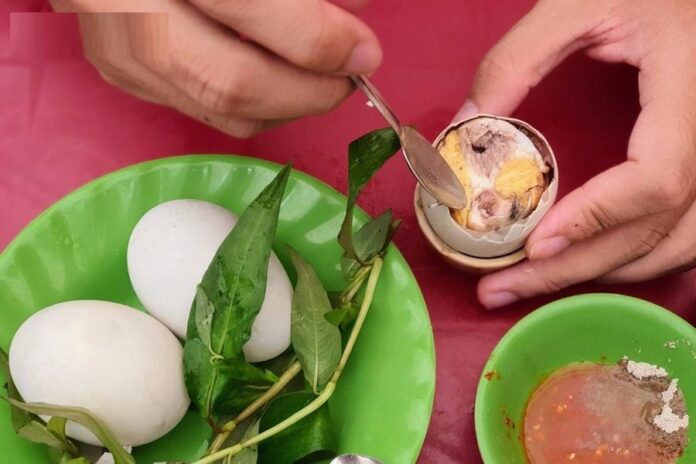
1. Individuals with High Blood Pressure
Balut contains high levels of cholesterol and fat, which can elevate blood pressure. For those with hypertension, consuming balut may increase the risk of stroke and heart attack. Moreover, eating it in the evening can further heighten these risks.
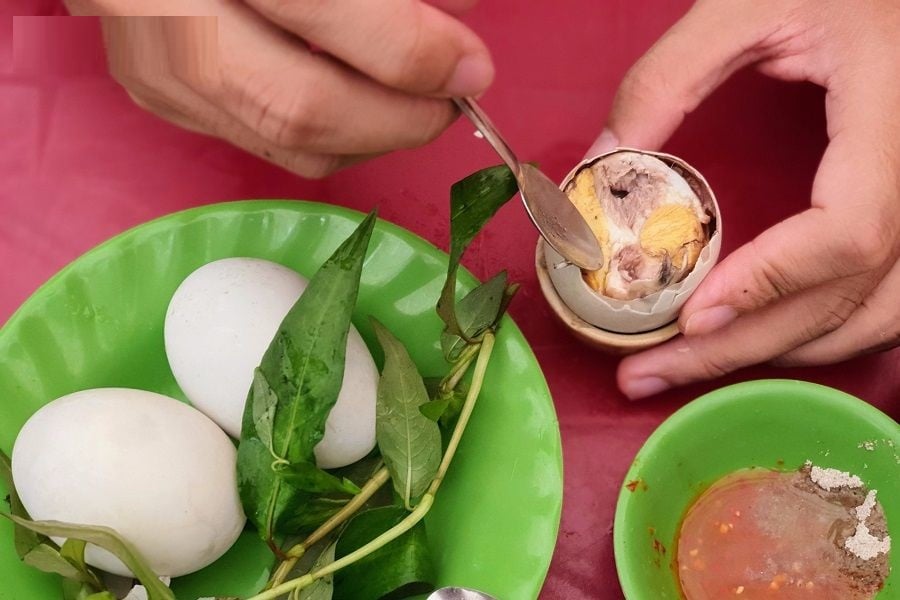

Balut: A Nutritious Treat But Not for Everyone – Know the Risks
2. Individuals with Cardiovascular Disease
Those with a history of cardiovascular disease should limit their intake of cholesterol-rich foods like balut. Excessive consumption can lead to clogged arteries, increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and heart failure.
3. Individuals with Digestive Disorders
Balut is difficult to digest and may cause bloating and abdominal discomfort. People with stomach ailments, inflammatory bowel disease, or other digestive issues should refrain from eating balut to prevent diarrhea and abdominal pain.
4. Individuals with Gout
The high protein content in balut can increase uric acid levels in the blood, triggering joint pain in individuals with gout. Overconsumption may exacerbate the condition and lead to more severe complications.
5. Individuals with Allergies
Some people may have allergic reactions to the proteins in balut, experiencing symptoms such as rashes, itching, and difficulty breathing. If you have previously exhibited allergic responses to eggs, it is advisable to steer clear of balut.
6. Pregnant Women in Their First Trimester
Although balut is highly nutritious, it is not recommended for pregnant women during their first trimester. Excessive consumption may cause bloating and indigestion, and it could potentially induce uterine contractions, posing risks to the fetus.

Balut: A Nutritious Treat But Not for Everyone – Know the Risks
How to Consume Balut for Optimal Health Benefits
-
For individuals without health concerns, it is advisable to limit consumption to 2-3 eggs per week, avoiding consecutive days.
-
Opt to eat balut in the morning to enhance absorption and prevent evening bloating.
-
Pair balut with Vietnamese coriander (rau răm) and ginger to balance its cooling properties.
While balut is a nutritious delicacy, it may not suit everyone. If you fall into any of the six categories mentioned above, it is prudent to limit or avoid consuming balut to safeguard your health and well-being.