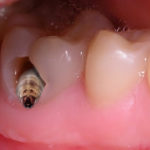
Cavities are a common issue among children with a sweet tooth, and it’s important for parents to be aware of the causes and how to care for their children’s dental health.
1. Causes of Cavities in Children
 Understanding the causes of cavities in children
Understanding the causes of cavities in children
Sweet Treats and Sugary Drinks
The main culprit behind cavities is often a child’s love for sweets and sugary drinks. The high sugar content in these treats can lead to tooth decay. Additionally, drinking juice, soda, or milk before bed can also contribute to cavity formation.
Inadequate Oral Hygiene Habits
Improper brushing techniques, insufficient brushing time, and lack of parental supervision can all lead to cavities. It’s important for children to use dental floss and mouthwash to remove food particles that get stuck between teeth and along the gum line.
Nighttime Bottle Feeding
Bottle feeding at night can cause cavities due to the prolonged exposure of teeth to sugar. The sugar in milk can remain on the teeth for hours, providing an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive and damage the teeth.
Fluoride Deficiency
 Fluoride deficiency can lead to cavities in children
Fluoride deficiency can lead to cavities in children
Fluoride is a natural mineral found in many foods and water sources. Children who consume water or use toothpaste without this mineral are at a higher risk of developing cavities. According to the American Dental Association (ADA), fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and helps fight against acid attacks. It can even help repair early stages of tooth decay.
However, parents should be cautious when using fluoride mouthwash for children under six years old, as they may accidentally swallow it. Close supervision is also recommended for children under 12 years of age when using fluoride products.
Health Issues
Respiratory problems can lead to mouth breathing, increasing the risk of cavities. Saliva plays a crucial role in preventing cavities by washing away food particles. When a child breathes through their mouth, it can lead to dry mouth, creating an ideal environment for cavity-causing bacteria to thrive.
2. Complications of Cavities in Children
 Understanding the complications of cavities in children
Understanding the complications of cavities in children
Cavities can cause significant discomfort for children, leading to irritability, sleep disturbances, and even weight loss or malnutrition. Additionally, cavities can affect the digestive system, particularly the stomach. If left untreated, cavities can lead to more severe complications, such as jawbone inflammation, abscesses in the mouth, and other serious infections.
Prolonged cavity issues can result in tooth abscesses, tooth loss, and difficulties with eating. As children grow, untreated cavities can also impact their facial development. In severe cases, cavities can lead to life-threatening complications such as cellulitis, sepsis, and even death.
If the infection spreads to the tooth’s pulp, it can cause periapical periodontitis, leading to headaches, heart and kidney problems, and joint pain. The resulting bad breath can also cause social anxiety and embarrassment for the child.
Parents should pay close attention to their children’s dental health and seek early intervention to prevent the destruction of the tooth pulp, which, once damaged, cannot be repaired, and the affected tooth will need to be extracted.
3. Proper Oral Care for Children
 Tips for proper oral care for children
Tips for proper oral care for children
According to TS.BS. Nguyen Thi Chau from the Center for Advanced Dental Medicine at Hanoi Medical University, here’s what you can do:
- Newborns to 12 Months: Gently wipe the gums with a clean cloth. As soon as the first teeth appear, use a soft-bristled toothbrush suitable for infants.
- 12 to 36 Months: Brush your child’s teeth twice a day for two minutes each time, using a soft-bristled toothbrush and a low-fluoride toothpaste recommended by a dentist.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks.
- Teach your child to use their tongue to remove food particles from their teeth immediately after eating.
- For children over one year old, regular dental check-ups every six months are recommended. This helps parents detect early signs of cavities and receive appropriate advice on diet and oral care for their children.
This article aims to provide parents with insights into childhood cavities and effective ways to maintain their children’s oral health.
Source: American Dental Association (ADA)