Common Types of Blood Cancer
1. Leukemia (approximately 36%)
According to Dr. Ha Hai Nam, Deputy Head of Abdominal Surgery I at K Tan Trieu Hospital in Hanoi, acute leukemia causes the body to produce a large number of immature white blood cells.
These abnormal cells clog the bone marrow, hindering the production of normal blood cells such as red blood cells and platelets. As a result, the immune system is severely weakened, increasing the risk of injury and infection. This condition is also known as “white blood disease.”
2. Lymphoma (approximately 46%)
Lymphocytes are present in many organs of the body, including lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, liver, stomach, and intestines. When these cells proliferate abnormally, they can cause the lymph nodes to become prominent and gradually enlarge, which is a common sign of lymphoma.
3. Myeloma (about 18%)
Myeloma is a disease related to plasma cells, which produce antibodies to help the body fight infections. When affected, these plasma cells grow uncontrollably, producing harmful antibodies.
As a consequence, patients may experience serious issues such as bone destruction, bone fractures, kidney failure, anemia, reduced platelet count, hypercalcemia, infections, and neurological disorders.
Subtle Signs of Blood Cancer
According to Dr. Nam, blood cancer is a dangerous disease with a lengthy treatment process and high costs. However, if detected early, the success rate of treatment can be as high as 90%. The following are some early warning signs of the disease that many people tend to overlook:
1. Digestive Symptoms
Leukemia cells can accumulate in the liver, kidneys, spleen, and intestines, leading to:
Persistent abdominal pain.
Loss of appetite and decreased food intake.
Frequent nausea.
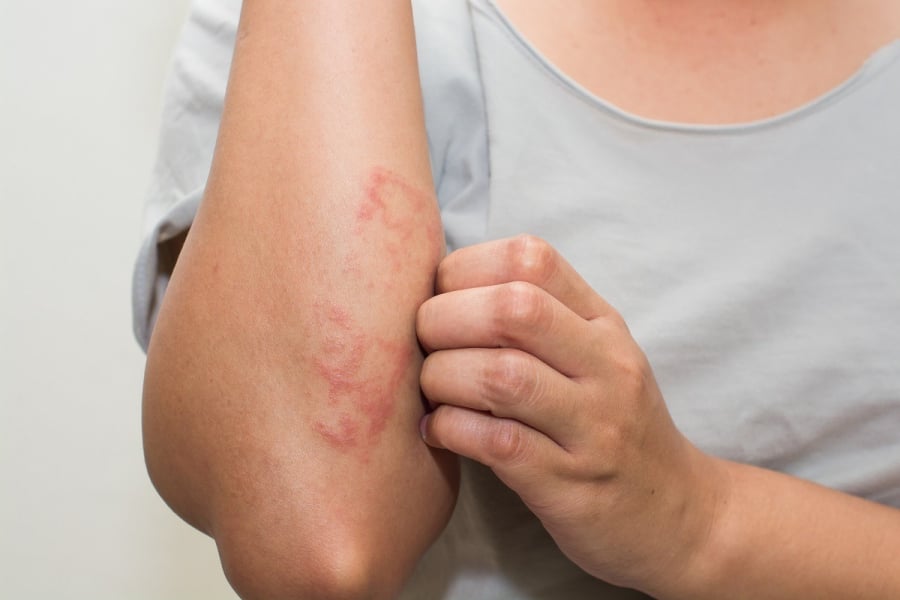
2. Coagulation and Bleeding Disorders
Due to a reduced platelet count, the body may experience:
Unexplained bruising that takes a long time to heal.
Appearance of tiny red dots (petechiae) on the skin and mucous membranes.
Nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and difficulty stopping bleeding.
3. Hypoxia
The decrease in red blood cells leads to oxygen deficiency in the body, resulting in:
Prolonged fatigue and unexplained weakness.
Sudden weight loss.
Headaches, chest discomfort, and shortness of breath.
4. Bone and Joint Symptoms
Persistent pain in areas such as knees, forearms, back, and shoulders.
Bone fractures occurring without significant trauma (pathological fractures)
5. Infection Signs
Persistent fever and chills without an apparent cause.
Night sweats.
Wounds that heal slowly and are prone to infection.
Itchy skin and unexplained rashes.
6. Swollen Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin that are painless and unresponsive to medication.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the chest or abdomen may cause chest discomfort, abdominal pain, and shortness of breath.
According to the American Cancer Society, there are approximately 175,000 new cases of blood cancer each year, accounting for about 10% of all cancers. Therefore, if you experience any of the mentioned symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for early detection and treatment, as recommended by Dr. Nam.