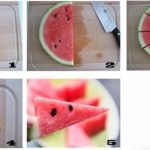
Bina vegetables
Chayote, also known as bina vegetables or chayote squash, contains a valuable nutrient called oxalic acid.
However, this compound affects the absorption of iron and calcium in the vegetable. Nevertheless, when cooked at high temperatures, this compound will be completely broken down. Cooking chayote squash thoroughly helps maximize the absorption of iron and calcium, especially for children’s height growth.

Mushrooms
When mushrooms are cooked well, they become more digestible, safe, and nutritious. With high temperatures, toxins in mushrooms are completely destroyed.
Moreover, mushrooms contain many nutrients such as potassium, niacin, zinc, and magnesium, and they will double in content during the cooking process.
Tomatoes
According to studies, cooking tomatoes will increase the lycopene content by up to 35%, an important antioxidant in tomatoes, which helps fight against various cancers such as prostate, pancreas, cervical, breast, and lung cancer, and reduces the risk of heart disease. Therefore, instead of eating them raw, cooking tomatoes will maximize the effectiveness of lycopene.

Carrots
The powerful antioxidant in carrots is carotenoids, and it increases by 14% when boiled or steamed at high temperatures.
Asparagus
To fully utilize the nutrients in asparagus, it needs to be cooked thoroughly before consumption. When cooked well, the level of phenolic acid in asparagus increases, which is an important factor related to reducing the risk of cancer.
Mung beans
Cooked mung beans have more benefits in reducing cholesterol compared to raw mung beans. However, to preserve the antioxidant properties of mung beans, it is best to cook them using methods such as baking, microwaving, grilling, or stir-frying instead of boiling or pressure cooking.