Eggs are a nutrient-rich food, offering a good source of protein, vitamins, and essential minerals. However, not all eggs are created equal, and consuming certain types of eggs can be harmful to your health. Here are six types of eggs that you should limit or avoid to maintain your well-being.
1. Raw or Undercooked Eggs
Raw or undercooked eggs may contain Salmonella bacteria, which can cause food poisoning with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. Nutritionists advise against consuming raw eggs or soft-boiled eggs with runny yolks, as the risk of bacterial contamination is high. Individuals with weakened immune systems, including young children, the elderly, and pregnant women, should be especially cautious. To ensure safety, eggs should be thoroughly cooked before consumption, with a particular focus on cooking the yolks completely to destroy any harmful bacteria.
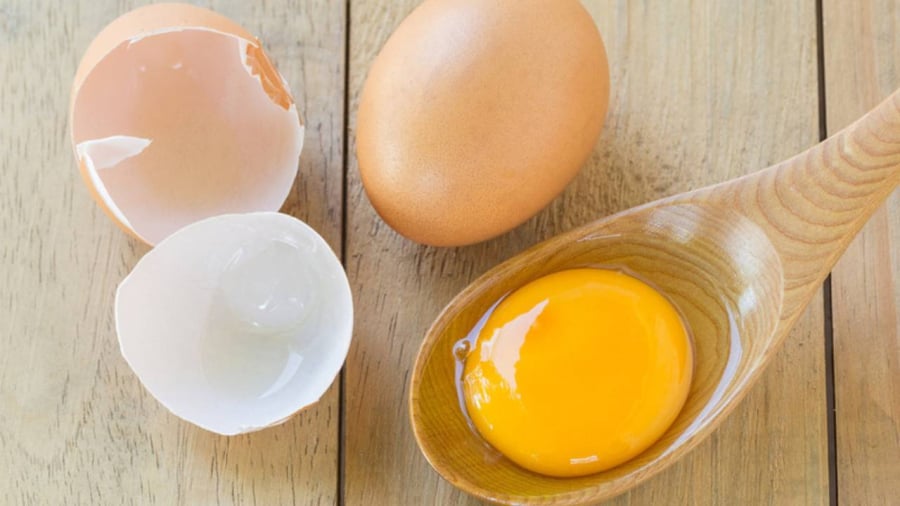

Raw Eggs
2. Salted Duck Eggs
Salted duck eggs are a popular delicacy in many cuisines, especially in Asia. While they offer a flavorful and tasty experience, these eggs contain extremely high levels of salt. Regular consumption of salted duck eggs can increase the risk of high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and kidney-related issues. The excessive sodium content can lead to water retention, causing swelling and placing additional strain on the circulatory system. Therefore, individuals with a history of heart disease or hypertension should limit their intake of salted duck eggs.
3. Tea Eggs
Tea eggs are a specialty in some countries, such as China and Taiwan. These eggs are cooked in a mixture of tea and spices, resulting in a unique and appealing flavor. However, tea eggs often contain high levels of preservatives and salt, which can be detrimental to health if consumed frequently. Moreover, the absorption of excessive caffeine from the tea in the eggs can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, and insomnia. Thus, tea eggs should be considered an occasional treat rather than a regular part of your diet.
4. Overcooked Hard-Boiled Eggs
Overcooking hard-boiled eggs, particularly when they are boiled for an extended period, causing the yolks to turn greenish-gray, can be harmful. When eggs are overcooked, the proteins undergo changes, forming iron hydrosulfide, a compound that can irritate the stomach and affect digestion. Additionally, overcooking reduces the nutritional value of the eggs, preventing the body from absorbing essential nutrients effectively. Regularly consuming overcooked hard-boiled eggs can lead to digestive issues and contribute to a feeling of fullness and bloating.
5. Pickled or Fermented Eggs
Pickled or fermented eggs are common in some cultures, especially in Eastern European countries. However, consuming eggs that have been fermented or pickled may not be beneficial for your health if they are not prepared and stored properly. The fermentation or pickling process can increase the risk of bacterial contamination and affect the quality of the eggs. Furthermore, these eggs typically have high acid content, and excessive consumption can damage the stomach lining and increase the risk of stomach and digestive disorders.
6. Fertilized Eggs
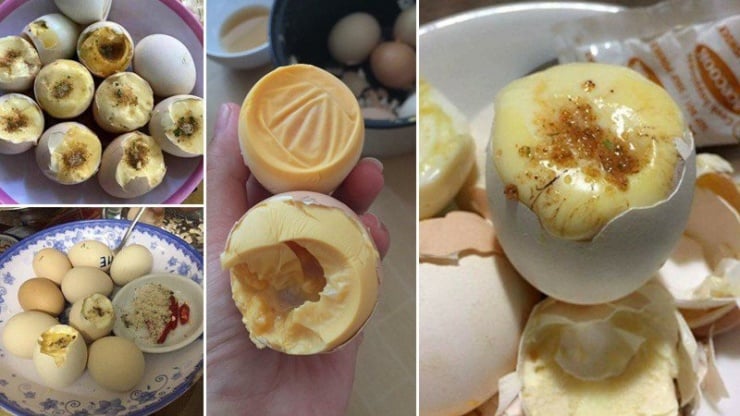

Fertilized Eggs
Nutrition experts warn that fertilized eggs are essentially rotten eggs that have been affected by temperature and environmental factors during the incubation process. At this point, the eggshell can no longer protect the egg, allowing bacteria to easily penetrate. Fertilized eggs have negligible nutritional value as the embryo has been destroyed, and bacterial toxins may be present. Even when boiled or fried, while the bacteria may be killed, their toxins can remain.
While there are anecdotal reports of people regularly consuming fertilized eggs without experiencing food poisoning, doctors explain that this could be due to their bodies having adapted to this practice over time. However, from a long-term health perspective, nutritionists advise against consuming fertilized eggs as they are not considered safe. Potential adverse effects include stomach upset, difficulty digesting, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, muscle pain, and even typhoid fever. Additionally, some toxins can accumulate in the liver, leading to conditions such as fatty liver and cirrhosis. Regular consumption of fertilized eggs can also result in bad breath due to the presence of hydrogen sulfide in the eggs.
Despite the reputation of eggs as a good source of protein and nutrients, it is crucial to make informed choices and practice safe handling and preparation. Avoid overconsuming unsafe eggs, such as raw, salted, tea-soaked, overcooked, pickled, or fertilized eggs. To maintain optimal health, opt for thoroughly cooked eggs without excessive additives or preservatives. Make smart food choices to sustain a healthy and peaceful life.