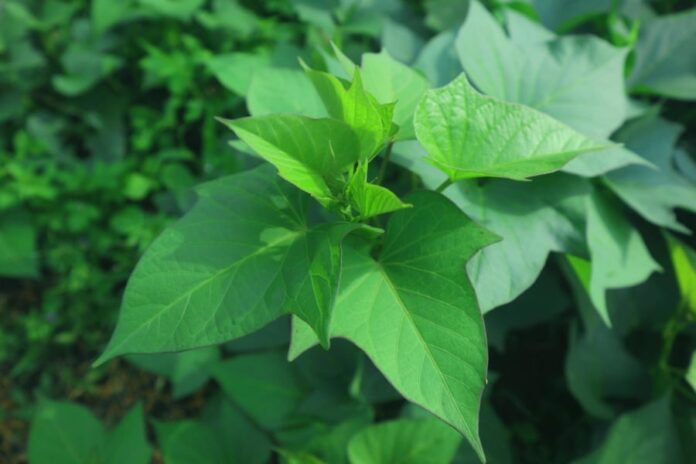
The two types of “immortal” vegetables mentioned here are sweet potato leaves and tamarind leaves.
Tamarind leaves used to grow wild in the fields. In the past, when there was a shortage of vegetables, people would pick and eat them.
Sweet potato leaves are also a rustic and inexpensive vegetable. In the past, people often cut these leaves to feed pigs.
However, nowadays, these two types of vegetables have become “immortal” because of their nutritional value and health benefits.
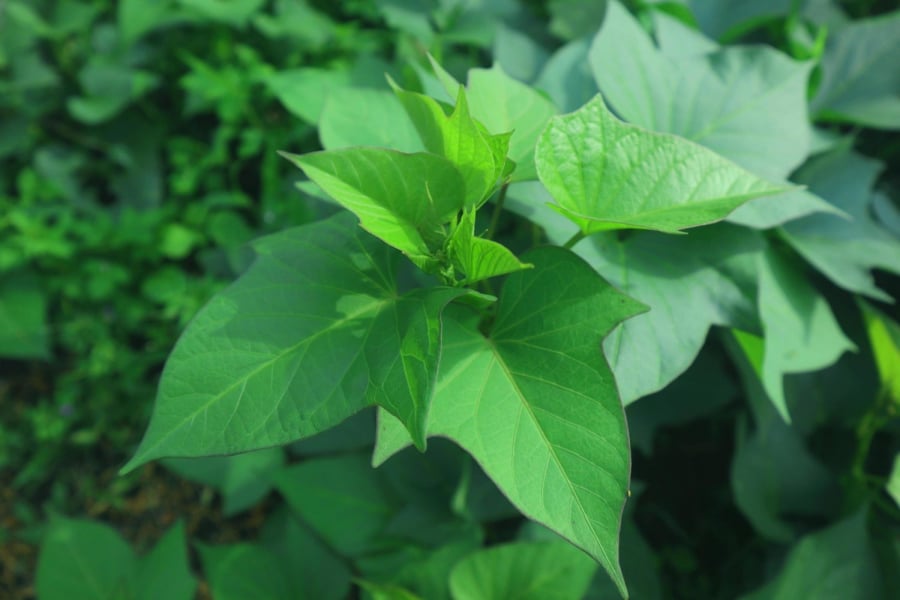

Sweet Potato Leaves
Health Benefits of Sweet Potato Leaves
According to Eastern medicine, sweet potato leaves are non-toxic, neutral in nature, and help boost health, improve eyesight, benefit the bile, and treat jaundice…
100g of sweet potato leaves can provide many nutrients, including 2kcal of energy, 91.8g of water, 2.6g of protein, 2.8g of starch, 11mg of vitamin C, 900mg of vitamin BB; 48mg of calcium, 54mg of phosphorus, and 2.7mg of iron…
Sweet potato leaves are a rich source of fiber, which helps detoxify and cool the body. They also contain high levels of chlorophyll, which helps purify the blood and remove toxins from the body.
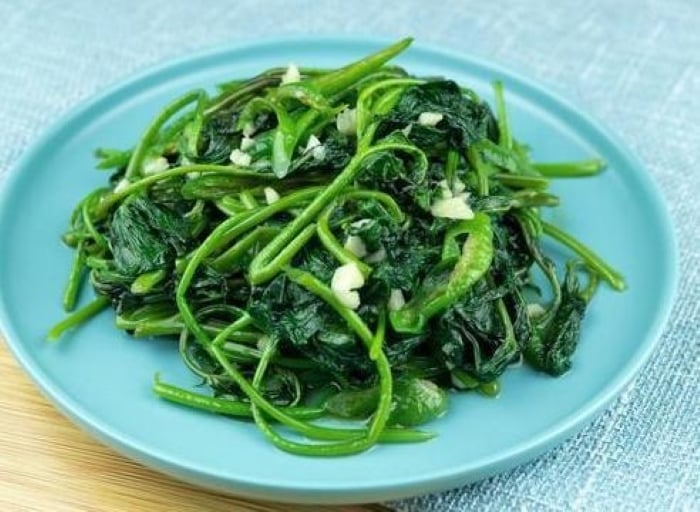

Stir-fried Sweet Potato Leaves with Garlic, a Favorite Dish of Many
Consuming sweet potato leaves regularly can also help prevent diabetes, combat obesity, and alleviate constipation. The protein in these leaves has antioxidant properties, helping to prolong life and improve skin health.
Health Benefits of Tamarind Leaves
Tamarind leaves have a sour taste, are non-toxic, and have a cold nature. They are rich in nutrients, and all parts of the plant, including the stems, leaves, and flower buds, can be used, except for the roots.
Tamarind leaves can be used to make salads, cooked in soups with lean meat, or stir-fried with garlic…
This vegetable is not only used as food but also as a medicinal herb with multiple benefits. Tamarind leaves can be consumed fresh or dried for later use.

Tamarind Leaves
Research has shown that tamarind leaves contain numerous nutrients beneficial to the human body. They include over 44 compounds such as flavonoids, alkaloids, terenoids, organic acids, vitamins, and minerals… Tamarind leaves are also rich in vitamin PP, vitamins B1, B2, C, and A, folic acid, choline, iron, magnesium, sodium, calcium, potassium, and oxalic acid…
Among these compounds, flavonoids are considered the primary and most biologically active compounds in tamarind leaves.
Tamarind leaves are regarded as a “longevity herb” due to their ability to treat various ailments. They possess anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, benefiting the skin, muscles, and bones, as well as cardiovascular health. Being cold in nature, tamarind leaves are excellent for cooling and detoxifying the body. They also aid in lowering blood sugar levels and promoting digestive health.
The presence of vitamins C, E, beta-carotene, alkaloids, and glutathione in tamarind leaves further contributes to their ability to combat free radicals and slow down the aging process.
The Ultimate Guide to the Super Leaf: Elevate Your Culinary Experience with This Secret Ingredient
The process of making Cha Xuong Song (Vietnamese herbal sausage) is quite simple and easy, similar to the popular Cha La Lot. However, the addition of the herb ‘Xương Sông’ (translated as ‘river bones’) gives this dish an aromatic and nutritious boost. With the inclusion of this herb, the humble family sausage takes on a whole new level of deliciousness and becomes a truly mouthwatering treat.
The Power of Eight: Unlocking Your Child’s Potential for Academic Success
Learning, getting smarter, and excelling in school is an exciting journey, and we’re here to help you navigate it with ease. This infographic guide will take you on an adventure, revealing the secrets to academic success and a brighter future. Get ready to unlock your true potential and soar to new heights!
The Noble Vegetable: A “Golden Medicinal Herb” as Valuable as Ginseng and Bird’s Nest, But Who Should Avoid It?
This humble vegetable, abundant in Vietnam, is a nutritional powerhouse, often hailed as a “golden medicinal herb” with equal nutritional value to ginseng and bird’s nest. Yet, despite its impressive health benefits, there are some important considerations to bear in mind to ensure its safe consumption and avoid any potential negative impact on one’s health.