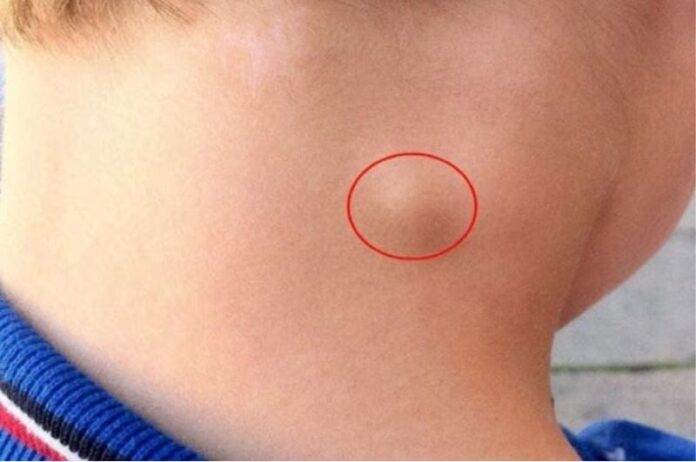
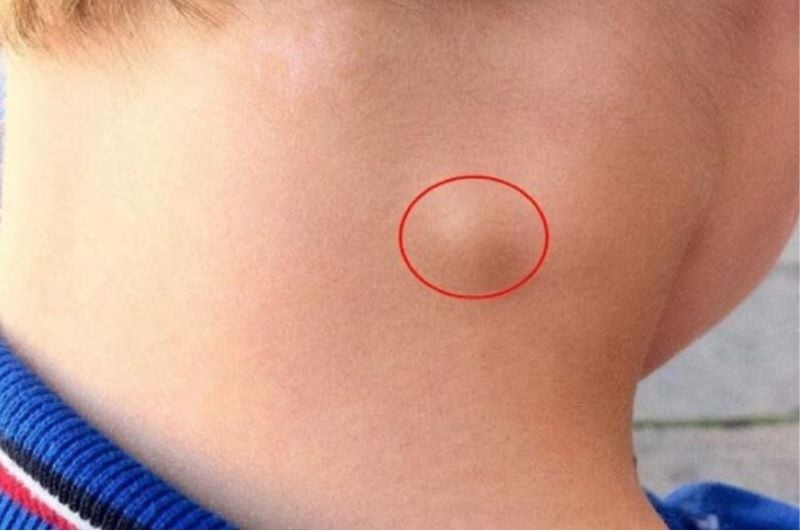
Painless Swelling of the Lymph Nodes
The first and most noticeable sign of lymph node cancer is the swelling of the lymph nodes, which typically appear in the neck, armpits, or groin. Unlike swollen glands due to infection, which are usually painful and subside within a few days, lymph nodes swollen due to cancer are often painless and gradually increase in size over time.
The lymph nodes can feel soft or hard, mobile or fixed to the surrounding tissue. In summary, if you notice any swelling that persists for more than two weeks, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Unexplained Weight Loss
If your body suddenly experiences rapid weight loss, typically amounting to 10% of your body weight within six months, and it is not due to a change in diet or deliberate weight loss efforts, this could be a warning sign. In lymph node cancer, cancerous cells grow rapidly and consume a significant amount of the body’s energy, resulting in unusual weight loss.
This is one of the classic “systemic” symptoms, often occurring in the early stages of the disease, but it is often overlooked or attributed to stress, insomnia, or reduced appetite.
Prolonged or Persistent Fever of Unknown Origin
A prolonged fever with no apparent cause is one of the manifestations of lymph node cancer. If you experience fever along with night sweats, chills, and prolonged fatigue despite adequate rest, do not hesitate to seek medical attention immediately.
Night Sweats
One of the fundamental characteristics of lymph node cancer is unusual night sweats. Patients may wake up in the middle of the night with drenched sleepwear and bedding, even in cool temperatures and without any apparent reason. If you frequently experience excessive sweating at night, it warrants caution.
This is not a typical “clammy hands and feet” phenomenon but rather the body’s reaction to inflammation or immune system changes due to the growth of cancerous cells.
Prolonged Itching or Rash
Some patients with lymph node cancer experience pervasive itching, a deep sensation of itching beneath the skin, which does not respond to conventional topical treatments. Additionally, red patches or itchy bumps may appear, particularly on the arms, legs, or chest. This is the immune system’s response to cancerous cells affecting the lymphatic vessels beneath the skin.