The Dangers of Consuming Meat Contaminated with Parasites
Cysticercus bovis and cysticercus cellulosae are the scientific terms for beef and pork contaminated with parasites. These parasites can have severe health consequences if consumed by humans.
There are various causes for the presence of these parasites in meat, primarily stemming from the animal’s food and water sources, which may contain larvae or eggs. Once ingested, the parasites can inhabit the gastrointestinal tract, with some being excreted and others entering the bloodstream and infecting the meat.
 Pork contaminated with parasites
Pork contaminated with parasites
Consuming meat infected with these parasites can lead to the development of larvae in the human body within 90 days. They inhabit the small intestine and stomach, causing gastrointestinal disorders. Mild symptoms include diarrhea and indigestion, while more severe cases can result in blood loss, neurological issues, fluid accumulation in organs, and even death due to extreme debilitation.

How to Identify Pork and Beef Contaminated with Parasites
It is possible to identify pork and beef contaminated with parasites through visual inspection or by touch:
– By touch: If the texture of the pork or beef feels stiff, lacking elasticity, and sticky or soft, it may be infected with parasites or treated with harmful chemicals like formaldehyde or urea.

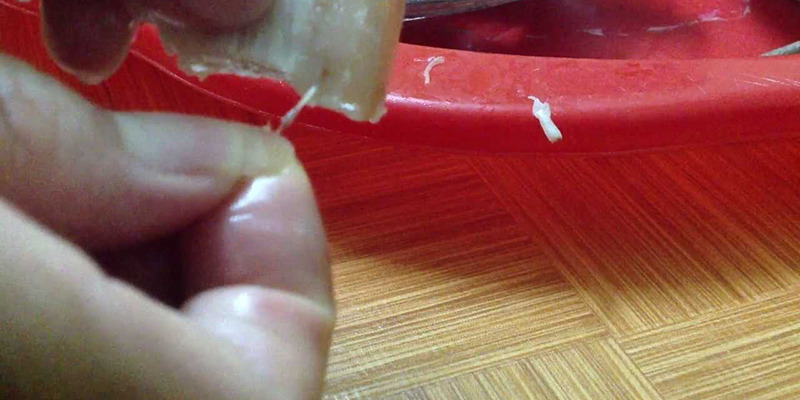
– Visual inspection: Cut the meat along the grain and inspect it. If you notice small white spots, about the size of a pinhead, the meat is likely infected with parasites. Alternatively, look for rice grain-sized, white or grayish, fiber- or oval-shaped marks running parallel to the meat grain.

If any of these signs are present, discard the meat immediately and do not consume it.
Safe Consumption of Pork and Beef
It is crucial to choose a trusted and safe source for purchasing meat, preferably from large supermarkets or department stores where the meat’s origin is known and properly stored.

Never consume undercooked or raw meat. Always cook thoroughly and eat immediately after cooking to prevent bacterial growth. Ensure proper sanitation of utensils, cutting boards, pots, and pans by sun-drying or boiling in hot water.
It is important to be cautious when purchasing meat from markets or street vendors, as the sources may be unclear, and the hygiene standards might not be up to par. Make informed choices and thoroughly inspect the meat before purchase to avoid any health risks associated with parasite-infected meat.