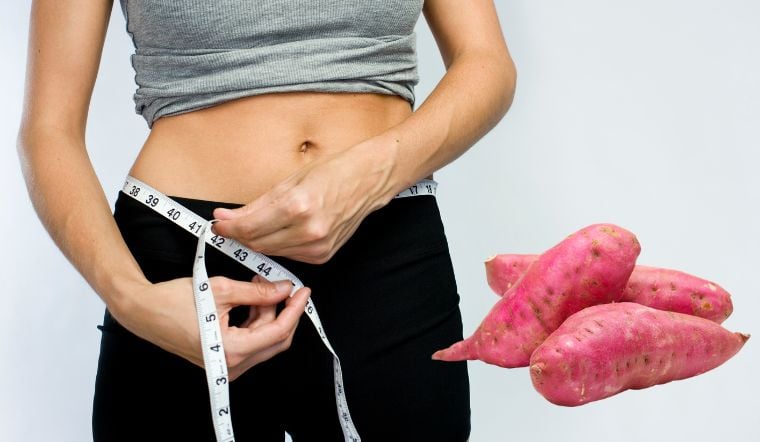
Sweet potatoes are a great source of soluble fiber, which aids digestion. This vibrant root vegetable boasts a significantly lower calorie count than white rice, making it an excellent substitute in daily meals.
The water content in sweet potatoes hydrates cells and supports metabolism, thereby limiting fat accumulation in the body. They are also a rich source of beneficial nutrients such as vitamin C, potassium, and calcium. Despite their nutritional density, sweet potatoes have a low glycemic index, with 100g containing only 85 calories and a glycemic load of 50.
## How to Eat Sweet Potatoes for Weight Loss: Expert-Recommended Tips
– **Eat the Skin**: The skin of a sweet potato is where most of the fiber, as well as sticky protein compounds, can be found. These compounds help lower blood cholesterol and have strong antioxidant effects, promoting healthier skin and overall well-being.
– **Cool Them After Cooking**: Once cooked, let them cool down and then refrigerate for 1-2 hours before consumption. This process forms resistant starch, which is harder to digest, thereby reducing calorie absorption and inducing a prolonged feeling of fullness.
– **Replace a Main Meal**: You can substitute 100g of steamed sweet potatoes, approximately 115 calories, for a main meal. This not only reduces calorie intake but also provides fiber and essential vitamins.
– **Choose Healthy Cooking Methods**: Steaming sweet potatoes at around 100°C not only retains their moisture but also maximizes the preservation of beneficial nutrients. For weight loss, avoid fried sweet potatoes as the added oil significantly increases the calorie count, counteracting your efforts.
## Common Mistakes to Avoid
– Do not consume raw or undercooked sweet potatoes as the starch in them may not be fully digested, leading to bloating and indigestion.
– Avoid eating sweet potatoes on an empty stomach as the acids they contain can irritate the stomach, causing a sense of fullness and nausea.
– While sweet potatoes are excellent for weight loss, they should not be your sole source of nutrition. Ensure you maintain a balanced diet, as excessive consumption of sweet potatoes can lead to increased calorie intake due to their starch content.

Sweet Potatoes: A Rich Source of Soluble Fiber for Digestive Health.