Can Sweet Potatoes With Sprouts Be Eaten?
According to nutrition experts, sweet potatoes that have sprouted do not produce toxins and can be consumed. However, it is recommended to peel off the sprouted parts and soak the potatoes in diluted salt water for about 10-15 minutes before cooking.
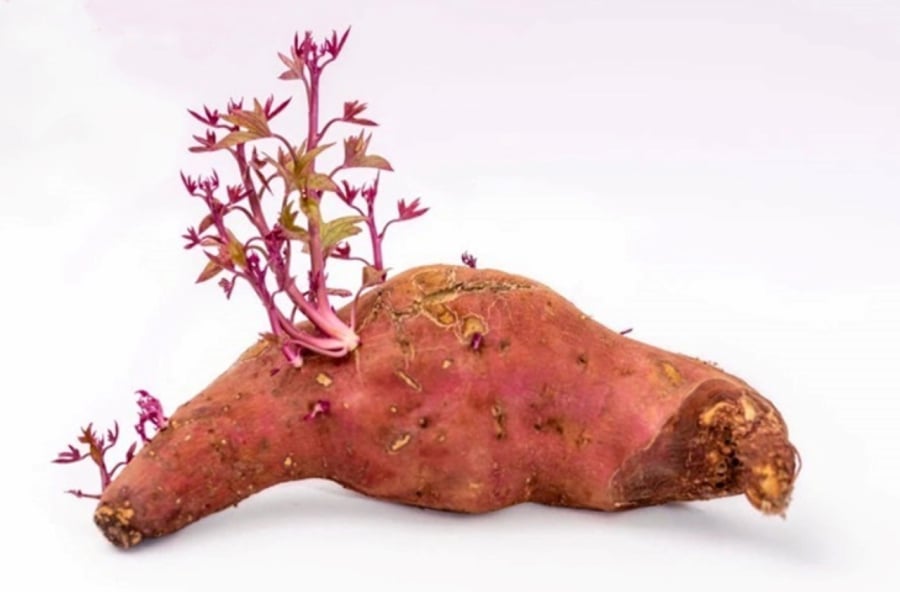

Sweet Potatoes With Sprouts Can Be Eaten, But the Longer They Are Kept, the More Nutrients Are Lost
In terms of nutritional value, sprouted sweet potatoes no longer contain the same amount of minerals or vitamins as they once did. The taste and flavor of the potatoes also change significantly and are not as delicious.
Although sprouted sweet potatoes do not produce toxins, they are prone to fungal infection. If you notice black or brown spots on the potatoes, they may be contaminated with the toxin ipomeamarone, produced by mold.
This toxin can cause stomach pain, vomiting, dizziness, and other symptoms. Therefore, it is not recommended for individuals with a weak digestive system, such as the elderly or children, to consume sprouted sweet potatoes.
As the sprouts grow, the sweet potatoes become drier, more fibrous, and lose their distinctive flavor.
What Should Be Done With Sprouted Sweet Potatoes?
Cut off the sprouts and soft parts of the potato: If the sweet potatoes have just started to sprout and the rest of the potato is still firm, you can cut off the sprouts and soft parts and use the remaining potato.
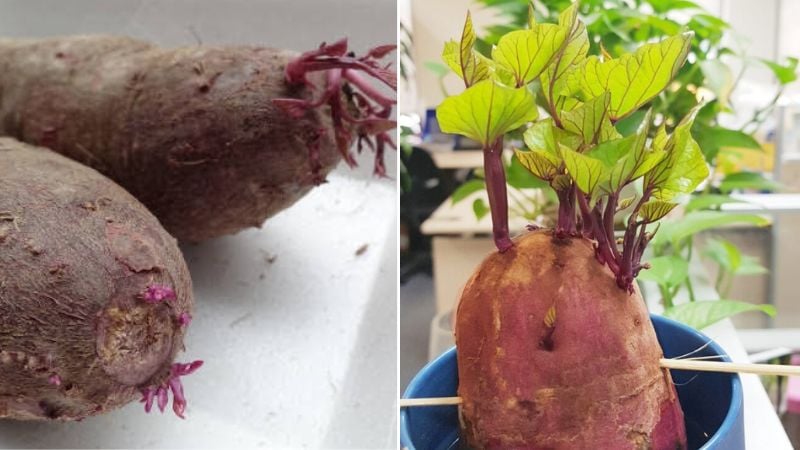

Sweet Potatoes With Sprouts Can Be Eaten But It’s Recommended to Limit Consumption
Use them as animal feed: Sprouted sweet potatoes can be fed to some types of livestock.
Plant them: If you wish to grow sweet potatoes, you can use the sprouted potatoes as seeds.
To store sweet potatoes for a longer period and maintain their quality, keep them in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place, away from direct sunlight.
While sprouted sweet potatoes can technically be eaten, it is advisable to limit their consumption to ensure your health and well-being.