Durian, known as the “king of fruits,” is a delicacy that captivates many. Despite its high price, consumers often end up with unripe, bland, or sparsely-fleshed durians.
When buying durian, should you choose one with thick or sparse spines?
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting durian is the shape and density of its spines. Many people wonder whether they should opt for a durian with thick or sparse spines.
The spines of a durian not only serve as a protective layer but also as an indicator of its ripeness and quality. The thickness or sparseness of the spines may be related to the flavor and sweetness of the fruit.
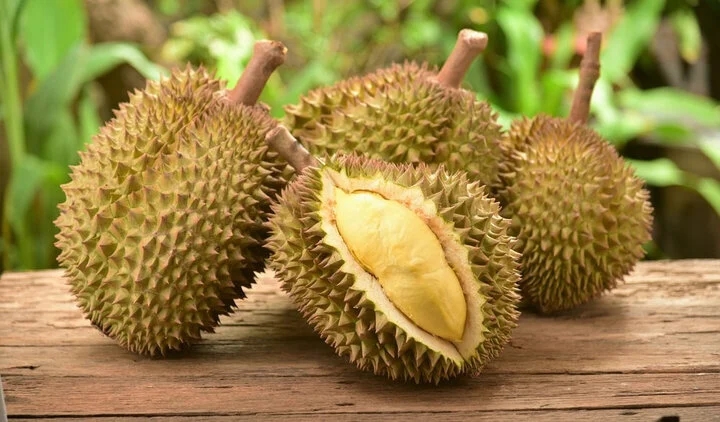

Should you choose durian with thick or sparse spines? (Photo: Emicakes)
To select a delicious durian, look for fruits with relatively large, short spines that are sparsely distributed. These are known as female durians.
When shopping, try pulling two adjacent spines together; if they spring back, the durian is likely ripe, with sweet flesh and a thin shell. If the spines are small, sharp, and densely packed, and pressing on them feels firm, the durian is probably unripe and may have unappetizing flesh.
Therefore, when buying durian, it is advisable to choose fruits with sparse spines.
Some tips for choosing delicious durian
In addition to observing the spines, here are some other factors to consider when selecting this exotic fruit.
Sense of Smell
Smell is crucial when choosing durian. To assess the quality, don’t skip the step of checking for its distinctive aroma. Ripe durians usually emit a strong, characteristic scent.
If you have to sniff closely to detect the aroma and also notice a pungent smell, the durian is likely unripe or forced-ripened, resulting in unappetizing flesh. On the other hand, if you detect a strong alcoholic odor, it means the durian is overripe and should be avoided.
Choose Heavy, Firm Fruits
The size and weight of durian matter, too. Heavier, firmer fruits often indicate evenly ripened durians with abundant flesh. Lighter fruits may be a sign of hollow or sparsely-fleshed durians.
Avoid Oddly Shaped Fruits
The shape of a durian can also provide clues about its quality. Well-shaped, plump durians with a rounded appearance and no deformities are usually a sign of delicious fruit. Such durians tend to have thin shells and sweet flesh.
Irregular shapes may indicate spoiled or unevenly ripened durians. Avoid choosing misshapen fruits with indentations, as they are likely to have fewer segments.
Inspect the Stem
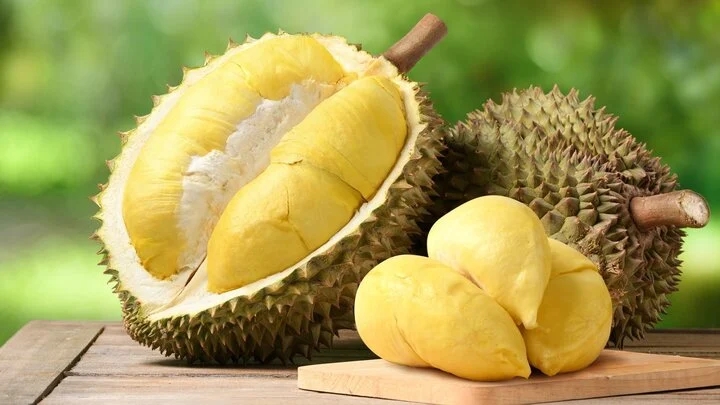

Opt for durians with fresh, securely attached stems. (Photo: Doveco)
Choose durians with relatively fresh stems that are firmly attached to the fruit. A fresh, green, and firm stem indicates a recently harvested durian that is still fresh and tasty. A dry, brown, or soft stem suggests that the durian has been stored for a while, and its flesh may not be as delicious as expected.
Listen for a Hollow Sound
Sound is another factor to consider when assessing durian quality. Hold the durian and gently shake it, or tap it lightly with a tool used to open the fruit.
If you hear a dull “thud” or a muffled sound, the durian is likely meaty and ripe, with thick flesh. However, if you hear a hollow “clang” or a ringing sound, it indicates a seed-heavy fruit that isn’t as tasty.
Inspect the Segments
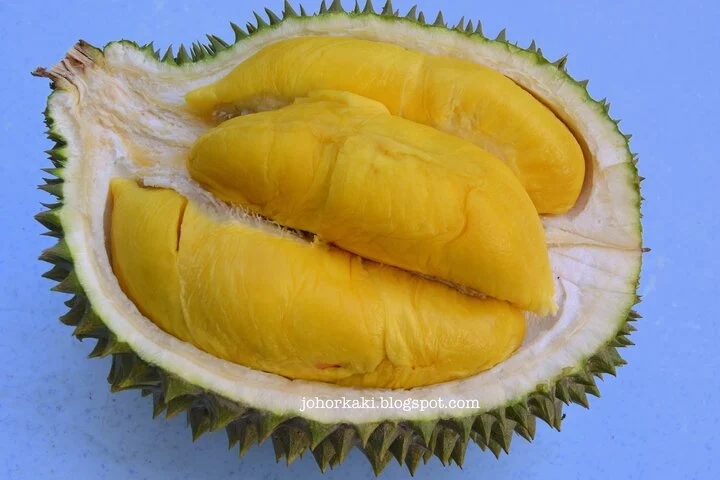

Ripe durian segments are deep yellow, soft, and fragrant. (Photo: Johor Kaki)
If possible, inspect the durian’s segments. Ripe segments are deep yellow, with soft, fragrant flesh. Unripe segments are usually pale, firm, and less aromatic.
Who Should Avoid Eating Durian?
While durian is delicious and offers health benefits, it’s not for everyone. The following groups should refrain from consuming this fruit.
– Pregnant Women: Durian’s high sugar content and “heating” nature can cause bloating and indigestion in pregnant women.
– People with Sore Throat, Cough, Cold, or Sensitive Airways: Durian’s heating properties and mucus-producing effects are not suitable for those with throat issues, coughs, colds, or sensitive airways. It’s also not recommended for those with constipation or hemorrhoids. Those with weak digestion may experience stomach discomfort after consuming durian.
– Diabetics, Obese Individuals, and Hypertensive Patients: With a high glycemic index (up to 70%), durian is rich in calories and can rapidly increase blood sugar levels. Therefore, it’s a fruit that diabetics must avoid. Obese individuals, hypertensive patients, and those with high cholesterol levels should also limit their consumption.
– People with Kidney or Heart Conditions: Durian’s high potassium content makes it unsuitable for individuals with kidney or heart problems. Potassium buildup in the body of someone with kidney failure can lead to life-threatening heart rhythm disorders.
According to VTC News